Improvement of gross motor and cognitive abilities by an exercise training program: three case reports
- PMID: 24672238
- PMCID: PMC3961067
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S58455
Improvement of gross motor and cognitive abilities by an exercise training program: three case reports
Abstract
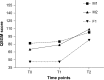
Background: This work examined the efficacy of an integrated exercise training program (coach and family) in three children with Down syndrome to improve their motor and cognitive abilities, in particular reaction time and working memory.
Methods: The integrated exercise training program was used in three children with Down syndrome, comprising two boys (M1, with a chronological age of 10.3 years and a mental age of 4.7 years; M2, with a chronological age of 14.6 years and a mental age of less than 4 years) and one girl (F1, chronological age 14.0 years and a mental age of less than 4 years).
Results: Improvements in gross motor ability scores were seen after the training period. Greater improvements in task reaction time were noted for both evaluation parameters, ie, time and omissions.
Conclusion: There is a close interrelationship between motor and cognitive domains in individuals with atypical development. There is a need to plan intervention programs based on the simultaneous involvement of child and parents and aimed at promoting an active lifestyle in individuals with Down syndrome.
Keywords: Down syndrome; cognitive abilities; disability; gross motor abilities; physical activity.
Figures
References
-
- Ziegler E. The retarded child as a whole person. In: Adams HE, Boardmna WK, editors. Advances in Experimental Child Psychology. New York, NY, USA: Pergamon; 1971. p. 1.
-
- Bellafiore M, Battaglia G, Bianco A, Paoli A, Farina F, Palma A. Improved postural control after dynamic balance training in older overweight women. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2011;23:378–385. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Bellafiore M, Bianco A, Paoli A, Palma A. Effects of a dynamic balance training protocol on podalic support in older women. Pilot study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2010;22:406–411. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources