Analyzing site selectivity in Rh2(esp)2-catalyzed intermolecular C-H amination reactions
- PMID: 24673332
- PMCID: PMC4004253
- DOI: 10.1021/ja5015508
Analyzing site selectivity in Rh2(esp)2-catalyzed intermolecular C-H amination reactions
Abstract
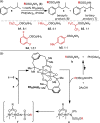
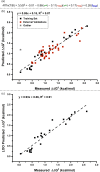
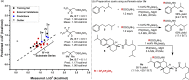
Predicting site selectivity in C-H bond oxidation reactions involving heteroatom transfer is challenged by the small energetic differences between disparate bond types and the subtle interplay of steric and electronic effects that influence reactivity. Herein, the factors governing selective Rh2(esp)2-catalyzed C-H amination of isoamylbenzene derivatives are investigated, where modification to both the nitrogen source, a sulfamate ester, and substrate are shown to impact isomeric product ratios. Linear regression mathematical modeling is used to define a relationship that equates both IR stretching parameters and Hammett σ(+) values to the differential free energy of benzylic versus tertiary C-H amination. This model has informed the development of a novel sulfamate ester, which affords the highest benzylic-to-tertiary site selectivity (9.5:1) observed for this system.
Figures





References
-
- Gutekunst W. R.; Baran P. S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1976–1991. - PubMed
-
- Wells P. R. Chem. Rev. 1963, 63, 171–219.
- Hansch C.; Leo A.; Taft R. W. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 165–195.
-
- Hammett L. P. Chem. Rev. 1935, 17, 125–136.
- Hammett L. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1937, 59, 96–103.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

