Heat shock proteins in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 24675290
- PMCID: PMC4012740
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1584
Heat shock proteins in multiple myeloma
Abstract
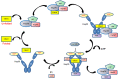
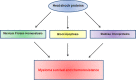
Heat shock proteins are molecular chaperones with a central role in protein folding and cellular protein homeostasis. They also play major roles in the development of cancer and in recent years have emerged as promising therapeutic targets. In this review, we discuss the known molecular mechanisms of various heat shock protein families and their involvement in cancer and in particular, multiple myeloma. In addition, we address the current progress and challenges in pharmacologically targeting these proteins as anti-cancer therapeutic strategies.
Figures

References
-
- Craig EA. Chaperones: helpers along the pathways to protein folding. Science. 1993;260(5116):1902–1903. - PubMed
-
- Hartl FU. Molecular chaperones in cellular protein folding. Nature. 1996;381(6583):571–579. - PubMed
-
- Hartl FU, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in the cytosol: from nascent chain to folded protein. Science. 2002;295(5561):1852–1858. - PubMed
-
- Udono H, Ichiyanagi T, Mizukami S, Imai T. Heat shock proteins in antigen trafficking--implications on antigen presentation to T cells. Int J Hyperthermia. 2009;25(8):617–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

