PET/SPECT imaging agents for neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 24676152
- PMCID: PMC4159420
- DOI: 10.1039/c3cs60430f
PET/SPECT imaging agents for neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
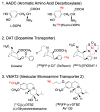
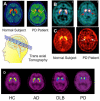
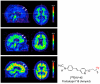
Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) or positron emission computed tomography (PET) imaging agents for neurodegenerative diseases have a significant impact on clinical diagnosis and patient care. The examples of Parkinson's Disease (PD) and Alzheimer's Disease (AD) imaging agents described in this paper provide a general view on how imaging agents, i.e. radioactive drugs, are selected, chemically prepared and applied in humans. Imaging the living human brain can provide unique information on the pathology and progression of neurodegenerative diseases, such as AD and PD. The imaging method will also facilitate preclinical and clinical trials of new drugs offering specific information related to drug binding sites in the brain. In the future, chemists will continue to play important roles in identifying specific targets, synthesizing target-specific probes for screening and ultimately testing them by in vitro and in vivo assays.
Figures




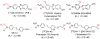
Similar articles
-
Imaging dopamine transporters in Parkinson's disease.Biomark Med. 2010 Oct;4(5):651-60. doi: 10.2217/bmm.10.86. Biomark Med. 2010. PMID: 20945978 Review.
-
New molecular targets for PET and SPECT imaging in neurodegenerative diseases.Braz J Psychiatry. 2012 Oct;34 Suppl 2:S125-36. doi: 10.1016/j.rbp.2012.07.002. Braz J Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23429844 Review. English, Portuguese.
-
Development of positron-emission tomography/single-photon emission computed tomography imaging probes for in vivo detection of beta-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's brains.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2009 Oct;57(10):1029-39. doi: 10.1248/cpb.57.1029. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2009. PMID: 19801854 Review.
-
Neuroprotection and imaging studies in Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009 Dec;15 Suppl 4:S33-7. doi: 10.1016/S1353-8020(09)70832-6. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009. PMID: 20123554 Review.
-
PET and SPECT in common neuropsychiatric disease.Clin Med (Lond). 2006 May-Jun;6(3):259-62. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.6-3-259. Clin Med (Lond). 2006. PMID: 16826858 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
PET neuroimaging studies of [(18)F]CABS13 in a double transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease and nonhuman primates.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Apr 15;6(4):535-41. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00055. Epub 2015 Mar 24. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25776827 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Brain Disorders: Focus on Neuroinflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 May;56(5):3295-3312. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1283-6. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30117106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Design of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Agents Binding to Amyloid Deposits.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 6;24(13):11152. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311152. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medicinal (Radio) Chemistry: Building Radiopharmaceuticals for the Future.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(34):5481-5534. doi: 10.2174/0929867331666230818092634. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37594105 Review.
-
Near-infrared fluorescent probes for imaging of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer׳s disease.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Jan;5(1):25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2014.12.006. Epub 2015 Jan 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Norenberg JP, Schwarz S, VanBrocklin H. J. Nucl. Med. 2011;52:16N. - PubMed
-
- Weissleder R. Science. 2006;312:1168–1171. - PubMed
-
- Hargreaves RJ, Rabiner EA. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013 - PubMed
-
- Rahmim A, Zaidi H. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2008;29:193–207. - PubMed
-
- Cherry S, Sorenson J, Phelps M. Physics in Nuclear Medicine. W.B. Saunders; New York: 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

