High blood pressure in children and its correlation with three definitions of obesity in childhood
- PMID: 24676372
- PMCID: PMC3987328
- DOI: 10.5935/abc.20130233
High blood pressure in children and its correlation with three definitions of obesity in childhood
Abstract
Background: Several authors have correlated the increase of cardiovascular risk with the nutritional status, however there are different criteria for the classification of overweight and obesity in children.
Objectives: To evaluate the performance of three nutritional classification criteria in children, as definers of the presence of obesity and predictors of high blood pressure in schoolchildren.
Methods: Eight hundred and seventeen children ranging 6 to 13 years old, enrolled in public schools in the municipality of Vila Velha (ES) were submitted to anthropometric evaluation and blood pressure measurement. The classification of the nutritional status was established by two international criteria (CDC/NCHS 2000 and IOTF 2000) and one Brazilian criterion (Conde e Monteiro 2006).
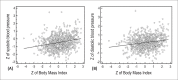
Results: The prevalence of overweight was higher when the criterion of Conde e Monteiro (27%) was used, and inferior by the IOTF (15%) criteria. High blood pressure was observed in 7.3% of children. It was identified a strong association between the presence of overweight and the occurrence of high blood pressure, regardless of the test used (p<0.001). The test showing the highest sensitivity in predicting elevated BP was the Conde e Monteiro (44%), while the highest specificity (94%) and greater overall accuracy (63%), was the CDC criterion.
Conclusions: The prevalence of overweight in Brazilian children is higher when using the classification criterion of Conde e Monteiro, and lower when the criterion used is IOTF. The Brazilian classification criterion proved to be the most sensitive predictor of high BP risk in this sample.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Sun SS, Grave GD, Siervogel RM, Pickoff AA, Arslanian SS, Daniels SR. Systolic blood pressure in childhood predicts hypertension and metabolic syndrome later in life. Pediatrics. 2007;119(2):237–246. - PubMed
-
- Sociedade Brasileira de Cardiologia. Sociedade Brasileira de Hipertensão. Sociedade Brasileira de Nefrologia VI Diretrizes brasileiras de hipertensão. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2010;95(1) supl. 1:1–51. - PubMed
-
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004;114(2) Suppl 4th Report:555–576. - PubMed
-
- da Silva MA, Rivera IR, de Souza MG, Carvalho AC. Blood pressure measurement in children and adolescents: guidelines of high blood pressure recommendations and current clinical practice. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2007;88(4):491–495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

