All trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) induces re-differentiation of early transformed breast epithelial cells
- PMID: 24676586
- PMCID: PMC4063534
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2354
All trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) induces re-differentiation of early transformed breast epithelial cells
Abstract
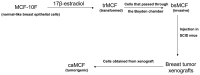
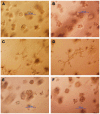
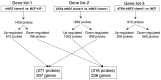
Retinoids have been used as potential chemotherapeutic or chemopreventive agents because of their differentiative, anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic and antioxidant properties. We investigated the effect of all trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) at different stages of the neoplastic transformation using an in vitro model of breast cancer progression. This model was previously developed by treating the MCF-10F human normal breast epithelial cells with high dose of estradiol and consists of four cell lines which show a progressive neoplastic transformation: MCF-10F, normal stage; trMCF, transformed MCF-10F; bsMCF, invasive stage; and caMCF, tumorigenic stage. In 3D cultures, MCF-10F cells form tubules resembling the structures in the normal mammary gland. After treatment with estradiol, these cells formed tubules and spherical masses which are indicative of transformation. Cells that only formed spherical masses in collagen were isolated (trMCF clone 11) and treated with ATRA. After treatment with 10 or 1 µM ATRA, the trMCF clone 11 cells showed tubules in collagen; 10 and 43% of the structures were tubules in cells treated with 10 and 1 µM ATRA, respectively. Gene expression studies showed that 207 genes upregulated in transformed trMCF clone 11 cells were downregulated after 1 µM ATRA treatment to levels comparable to those found in the normal breast epithelial cells MCF-10F. Furthermore, 236 genes that were downregulated in trMCF clone 11 were upregulated after 1 µM ATRA treatment to similar levels shown in normal epithelial cells. These 443 genes defined a signature of the ATRA re-programming effect. Our results showed that 1 µM ATRA was able to re-differentiate transformed cells at early stages of the neoplastic process and antagonistically regulate breast cancer associated genes. The invasive and tumorigenic cells did not show any changes in morphology after ATRA treatment. These results suggest that ATRA could be used as a chemopreventive agent to inhibit the progression of premalignant lesions of the breast.
Figures



References
-
- Mongan NP, Gudas LJ. Diverse actions of retinoid receptors in cancer prevention and treatment. Differentiation. 2007;75:853–870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

