Role of podocyte B7-1 in diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 24676639
- PMCID: PMC4073425
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013050518
Role of podocyte B7-1 in diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
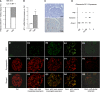
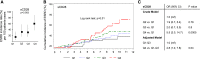
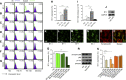
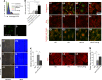
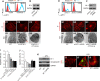
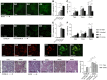
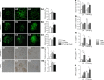
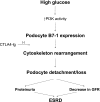
Podocyte injury and resulting albuminuria are hallmarks of diabetic nephropathy, but targeted therapies to halt or prevent these complications are currently not available. Here, we show that the immune-related molecule B7-1/CD80 is a critical mediator of podocyte injury in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. We report the induction of podocyte B7-1 in kidney biopsy specimens from patients with type 2 diabetes. Genetic and epidemiologic studies revealed the association of two single nucleotide polymorphisms at the B7-1 gene with diabetic nephropathy. Furthermore, increased levels of the soluble isoform of the B7-1 ligand CD28 correlated with the progression to ESRD in individuals with type 2 diabetes. In vitro, high glucose conditions prompted the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase-dependent upregulation of B7-1 in podocytes, and the ectopic expression of B7-1 in podocytes increased apoptosis and induced disruption of the cytoskeleton that were reversed by the B7-1 inhibitor CTLA4-Ig. Podocyte expression of B7-1 was also induced in vivo in two murine models of diabetic nephropathy, and treatment with CTLA4-Ig prevented increased urinary albumin excretion and improved kidney pathology in these animals. Taken together, these results identify B7-1 inhibition as a potential therapeutic strategy for the prevention or treatment of diabetic nephropathy.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Olshansky SJ, Passaro DJ, Hershow RC, Layden J, Carnes BA, Brody J, Hayflick L, Butler RN, Allison DB, Ludwig DS: A potential decline in life expectancy in the United States in the 21st century. N Engl J Med 352: 1138–1145, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Tirosh A, Shai I, Tekes-Manova D, Israeli E, Pereg D, Shochat T, Kochba I, Rudich A, Israeli Diabetes Research Group : Normal fasting plasma glucose levels and type 2 diabetes in young men. N Engl J Med 353: 1454–1462, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Fiorina P, Folli F, Bertuzzi F, Maffi P, Finzi G, Venturini M, Socci C, Davalli A, Orsenigo E, Monti L, Falqui L, Uccella S, La Rosa S, Usellini L, Properzi G, Di Carlo V, Del Maschio A, Capella C, Secchi A: Long-term beneficial effect of islet transplantation on diabetic macro-/microangiopathy in type 1 diabetic kidney-transplanted patients. Diabetes Care 26: 1129–1136, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Nakamura T, Ushiyama C, Suzuki S, Hara M, Shimada N, Ebihara I, Koide H: Urinary excretion of podocytes in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15: 1379–1383, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Reiser J, von Gersdorff G, Loos M, Oh J, Asanuma K, Giardino L, Rastaldi MP, Calvaresi N, Watanabe H, Schwarz K, Faul C, Kretzler M, Davidson A, Sugimoto H, Kalluri R, Sharpe AH, Kreidberg JA, Mundel P: Induction of B7-1 in podocytes is associated with nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest 113: 1390–1397, 2004 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK057683/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58549/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK091218/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091218/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062472/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK041526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073495/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK101350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK073495/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058549/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57683/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK089394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK77532/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK41526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK077532/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007726/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32DK007726-28/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK062472/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP000123/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

