METTL21C is a potential pleiotropic gene for osteoporosis and sarcopenia acting through the modulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 24677265
- PMCID: PMC4074268
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.2200
METTL21C is a potential pleiotropic gene for osteoporosis and sarcopenia acting through the modulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
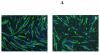
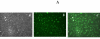
Sarcopenia and osteoporosis are important public health problems that occur concurrently. A bivariate genome-wide association study (GWAS) identified METTL21c as a suggestive pleiotropic gene for both bone and muscle. The METTL21 family of proteins methylates chaperones involved in the etiology of both myopathy and inclusion body myositis with Paget's disease. To validate these GWAS results, Mettl21c mRNA expression was reduced with siRNA in a mouse myogenic C2C12 cell line and the mouse osteocyte-like cell line MLO-Y4. At day 3, as C2C12 myoblasts start to differentiate into myotubes, a significant reduction in the number of myocytes aligning/organizing for fusion was observed in the siRNA-treated cells. At day 5, both fewer and smaller myotubes were observed in the siRNA-treated cells as confirmed by histomorphometric analyses and immunostaining with myosin heavy chain (MHC) antibody, which only stains myocytes/myotubes but not myoblasts. Intracellular calcium (Ca(2+)) measurements of the siRNA-treated myotubes showed a decrease in maximal amplitude peak response to caffeine, suggesting that less Ca(2+) is available for release due to the partial silencing of Mettl21c, correlating with impaired myogenesis. In siRNA-treated MLO-Y4 cells, 48 hours after treatment with dexamethasone there was a significant increase in cell death, suggesting a role of Mettl21c in osteocyte survival. To investigate the molecular signaling machinery induced by the partial silencing of Mettl21c, we used a real-time PCR gene array to monitor the activity of 10 signaling pathways. We discovered that Mettl21c knockdown modulated only the NF-κB signaling pathway (ie, Birc3, Ccl5, and Tnf). These results suggest that Mettl21c might exert its bone-muscle pleiotropic function via the regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is critical for bone and muscle homeostasis. These studies also provide rationale for cellular and molecular validation of GWAS, and warrant additional in vitro and in vivo studies to advance our understanding of role of METTL21C in musculoskeletal biology.
Keywords: BONE-MUSCLE INTERACTIONS; GENETIC RESEARCH; HUMAN ASSOCIATION STUDIES; OSTEOCYTES; SKELETAL MUSCLE.
© 2014 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Figures







References
-
- Bijlsma AY, Meskers CG, Westendorp RG, Maier AB. Chronology of age-related disease definitions: osteoporosis and sarcopenia. Ageing Res Rev. 2012;11(2):320–4. - PubMed
-
- Janssen I, Shepard DS, Katzmarzyk PT, Roubenoff R. The healthcare costs of sarcopenia in the United States. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(1):80–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

