A review of organic and inorganic biomaterials for neural interfaces
- PMID: 24677434
- PMCID: PMC4373558
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201304496
A review of organic and inorganic biomaterials for neural interfaces
Abstract
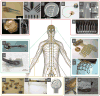
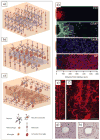
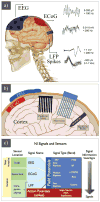
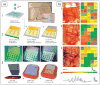
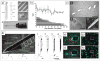
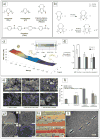
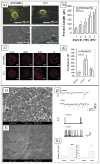
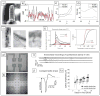
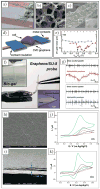
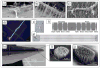
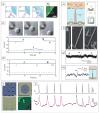
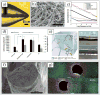
Recent advances in nanotechnology have generated wide interest in applying nanomaterials for neural prostheses. An ideal neural interface should create seamless integration into the nervous system and performs reliably for long periods of time. As a result, many nanoscale materials not originally developed for neural interfaces become attractive candidates to detect neural signals and stimulate neurons. In this comprehensive review, an overview of state-of-the-art microelectrode technologies provided fi rst, with focus on the material properties of these microdevices. The advancements in electro active nanomaterials are then reviewed, including conducting polymers, carbon nanotubes, graphene, silicon nanowires, and hybrid organic-inorganic nanomaterials, for neural recording, stimulation, and growth. Finally, technical and scientific challenges are discussed regarding biocompatibility, mechanical mismatch, and electrical properties faced by these nanomaterials for the development of long-lasting functional neural interfaces.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

