Age-related changes in astrocytic and ependymal cells of the subventricular zone
- PMID: 24677590
- PMCID: PMC4322944
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.22642
Age-related changes in astrocytic and ependymal cells of the subventricular zone
Abstract
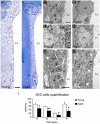
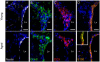
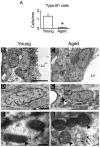
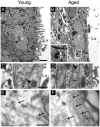
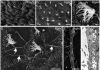
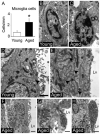
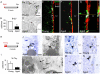
Neurogenesis persists in the adult subventricular zone (SVZ) of the mammalian brain. During aging, the SVZ neurogenic capacity undergoes a progressive decline, which is attributed to a decrease in the population of neural stem cells (NSCs). However, the behavior of the NSCs that remain in the aged brain is not fully understood. Here we performed a comparative ultrastructural study of the SVZ niche of 2-month-old and 24-month-old male C57BL/6 mice, focusing on the NSC population. Using thymidine-labeling, we showed that residual NSCs in the aged SVZ divide less frequently than those in young mice. We also provided evidence that ependymal cells are not newly generated during senescence, as others studies suggest. Remarkably, both astrocytes and ependymal cells accumulated a high number of intermediate filaments and dense bodies during aging, resembling reactive cells. A better understanding of the changes occurring in the neurogenic niche during aging will allow us to develop new strategies for fighting neurological disorders linked to senescence.
Figures
References
-
- Achanta P, Capilla-Gonzalez V, Purger D, Reyes J, Sailor K, Song H, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Gonzalez-Perez O, Ford E, Quinones-Hinojosa A. Subventricular zone localized irradiation affects the generation of proliferating neural precursor cells and the migration of neuroblasts. Stem Cells. 2012;30:2548–2560. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batiz LF, Jimenez AJ, Guerra M, Rodriguez-Perez LM, Toledo CD, Vio K, Paez P, Perez-Figares JM, Rodriguez EM. New ependymal cells are born postnatally in two discrete regions of the mouse brain and support ven tricular enlargement in hydrocephalus. Acta Neuropathol. 2011;121:721–735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

