Anchoring a cytoactive factor in a wound bed promotes healing
- PMID: 24677775
- PMCID: PMC4219926
- DOI: 10.1002/term.1886
Anchoring a cytoactive factor in a wound bed promotes healing
Abstract
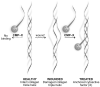
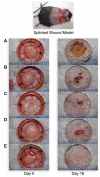
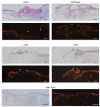
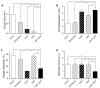
Wound healing is a complex process that requires the intervention of cytoactive factors. The one-time application of soluble factors to a wound bed does not maintain a steady, sufficient concentration. Here we investigated the benefits of anchoring a factor in a wound bed via a tether to endogenous collagen. We used a collagen-mimetic peptide (CMP) as a pylon. The CMP binds to damaged but not intact collagen and thus localizes a pendant cytoactive factor in the regions of a wound bed that require intervention. As a model factor, we chose substance P, a peptide of the tachykinin family that promotes wound healing. Using splinted wounds in db/db mice, we found that the one-time application of a CMP-substance P conjugate enhances wound healing compared to unconjugated substance P and other controls. Specifically, all 16 wounds treated with the conjugate closed more thoroughly and, did so with extensive re-epithelialization and mitigated inflammatory activity. These data validate a simple and general strategy for re-engineering wound beds by the integration of beneficial cytoactive factors. Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Keywords: Mus musculus; Substance P; collagen; extracellular matrix; peptide; synthetic biology.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Ananthanarayanan VS, Orlicky S. Interaction of substance P and its N- and C-terminal fragments with Ca2+: Implications for hormone action. Biopolymers. 1992;32:1765–1773. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Shavit Z, Goldman R, Stabinsky Y, et al. Enhancement of phagocytosis—A newly found activity of substance P residing in its N-terminal tetrapeptide sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980;94:1445–1451. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O, Golinko MS, et al. Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Rep Regen. 2008;16:585–601. - PubMed
-
- Baum CL, Arpey CJ. Normal cutaneous wound healing: Clinical correlation with cellular and molecular events. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:674–686. - PubMed
-
- Brem H, Tomic-Canic M, Entero H, et al. The synergism of age and db/db genotype impairs wound healing. Exp Gerontol. 2007;42:523–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

