Bioreducible polycations in nucleic acid delivery: past, present, and future trends
- PMID: 24678057
- PMCID: PMC4410047
- DOI: 10.1002/mabi.201400061
Bioreducible polycations in nucleic acid delivery: past, present, and future trends
Abstract
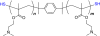
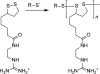
Polycations that are degradable by reduction of disulfide bonds are developed for applications in delivery of nucleic acids. This Feature Article surveys methods of synthesis of bioreducible polycations and discusses current understanding of the mechanism of action of bioreducible polyplexes. Emphasis is placed on the relationship between the biological redox environment and toxicity, trafficking, transfection activity, and in vivo behavior of bioreducible polycations and polyplexes.
Keywords: bioreducible; disulfides; gene delivery; polycations; polyplexes.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures





References
-
- Bang EK, Lista M, Sforazzini G, Sakai N, Matile S. Chem. Sci. 2012;3:1752.
-
- Wu AM, Senter PD. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:1137. - PubMed
-
- Corbett PT, Leclaire J, Vial L, West KR, Wietor J-L, Sanders JK, Otto S. Chem. Rev. 2006;106:3652. - PubMed
-
- Yoon JA, Kamada J, Koynov K, Mohin J, Nicolaÿ R, Zhang Y, Balazs AC, Kowalewski T, Matyjaszewski K. Macromolecules. 2011;45:142.
-
- Otto S, Furlan RL, Sanders JK. Science. 2002;297:590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

