Hyaluronan and synovial joint: function, distribution and healing
- PMID: 24678248
- PMCID: PMC3967437
- DOI: 10.2478/intox-2013-0019
Hyaluronan and synovial joint: function, distribution and healing
Abstract
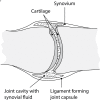
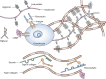
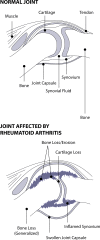
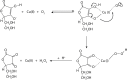
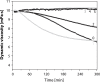
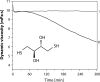
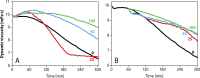
Synovial fluid is a viscous solution found in the cavities of synovial joints. The principal role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articular cartilages of synovial joints during movement. The presence of high molar mass hyaluronan (HA) in this fluid gives it the required viscosity for its function as lubricant solution. Inflammation oxidation stress enhances normal degradation of hyaluronan causing several diseases related to joints. This review describes hyaluronan properties and distribution, applications and its function in synovial joints, with short review for using thiol compounds as antioxidants preventing HA degradations under inflammation conditions.
Keywords: antioxidant; hyaluronan; synovial joint fluid; thiol compound.
Figures
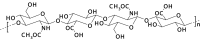



References
-
- Abeydeera LR. In vitro production of embryos in swine. Theriogenology. 2002;57:257–273. - PubMed
-
- Adams ME. Viseosupplementation: A treatment for osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1993;20(Suppl. 39):1–24. - PubMed
-
- Altman RD. Intra-articular sodium hyaluronate in osteoarthritis of the knee. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2000;30:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Hoey BM, Butler J. The antioxidant action of N-acetylcysteine: its reaction with hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, superoxide, and hypochlorous acid. Free Radic Biol Med. 1989;6:593. - PubMed
-
- Ashhurst DE, Bland YS, Levick JR. An immunohistochemical study of the collagens of rabbit synovial interstitium. J Rheumatol. 1991;18:1669–1672. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
