Low-bit rate feedback strategies for iterative IA-precoded MIMO-OFDM-based systems
- PMID: 24678274
- PMCID: PMC3942422
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/619454
Low-bit rate feedback strategies for iterative IA-precoded MIMO-OFDM-based systems
Abstract
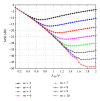
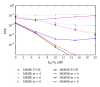
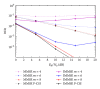
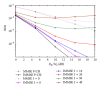
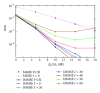
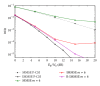
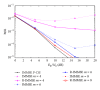
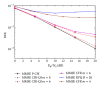
Interference alignment (IA) is a promising technique that allows high-capacity gains in interference channels, but which requires the knowledge of the channel state information (CSI) for all the system links. We design low-complexity and low-bit rate feedback strategies where a quantized version of some CSI parameters is fed back from the user terminal (UT) to the base station (BS), which shares it with the other BSs through a limited-capacity backhaul network. This information is then used by BSs to perform the overall IA design. With the proposed strategies, we only need to send part of the CSI information, and this can even be sent only once for a set of data blocks transmitted over time-varying channels. These strategies are applied to iterative MMSE-based IA techniques for the downlink of broadband wireless OFDM systems with limited feedback. A new robust iterative IA technique, where channel quantization errors are taken into account in IA design, is also proposed and evaluated. With our proposed strategies, we need a small number of quantization bits to transmit and share the CSI, when comparing with the techniques used in previous works, while allowing performance close to the one obtained with perfect channel knowledge.
Figures


References
-
- Gesbert D, Hanly S, Huang H, Shamai S, Simeone O, Yu W. Multi-cell MIMO cooperative networks: a new look at interference. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications. 2010;28(9):1380–1408.
-
- Castanheira D, Gameiro A. Distributed antenna system capacity scaling. IEEE Wireless Communications. 2010;17(3):68–75.
-
- 3GPP. Coordinated multi-point operation for LTE physical layer aspects. 2011;(3GPP TR 36. 819)
-
- Maddah-Ali MA, Motahari AS, Khandani AK. Communication over MIMO X channels: interference alignment, decomposition, and performance analysis. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory. 2008;54(8):3457–3470.
-
- Cadambe VR, Jafar SA. Interference alignment and degrees of freedom of the K-user interference channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory. 2008;54(8):3425–3441.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

