TLR/NCR/KIR: Which One to Use and When?
- PMID: 24678311
- PMCID: PMC3958761
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00105
TLR/NCR/KIR: Which One to Use and When?
Abstract
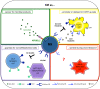
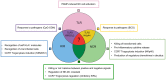
By means of a complex receptor array, Natural killer (NK) cells can recognize variable patterns of ligands and regulate or amplify accordingly their effector functions. Such NK receptors include old, rather conserved, molecules, such as toll-like receptors (TLRs), which enable NK cells to respond both to viral and bacterial products, and newer and evolving molecules, such as killer Ig-like receptors and natural cytotoxicity receptors, which control NK cytotoxicity and are responsible for the elimination of virus-infected or tumor cells without damaging self-unaltered cells. In addition, to rapidly gain new functions NK cells also can acquire new receptors by trogocytosis. Thus, NK cells may have adapted their receptors to different functional needs making them able to play a key role in the modulation of critical events occurring in several compartments of human body (primarily in SLCs but also in decidua during pregnancy). In this review, we will discuss on how the various types of receptors can be used to address specific functions in different immunological contexts.
Keywords: CCR7; KIR; NCR; NK cell; TLR; anti-tumor response; anti-viral response; innate immunity.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources