Molecular diagnosis of sepsis: New aspects and recent developments
- PMID: 24678402
- PMCID: PMC3955828
- DOI: 10.1556/EuJMI.4.2014.1.1
Molecular diagnosis of sepsis: New aspects and recent developments
Abstract
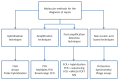
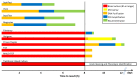
By shortening the time to pathogen identification and allowing for detection of organisms missed by blood culture, new molecular methods may provide clinical benefits for the management of patients with sepsis. While a number of reviews on the diagnosis of sepsis have recently been published we here present up-to-date new developments including multiplex PCR, mass spectrometry and array techniques. We focus on those techniques that are commercially available and for which clinical studies have been performed and published.
Keywords: PCR; SeptiFast; biomarker; blood culture; mass spectrometry; microarray; molecular diagnostics; sepsis.
Figures
References
-
- Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013 Aug 29;369(9):840–581. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, Osborn TM, Nunnally ME, Townsend SR, Reinhart K, Kleinpell RM, Angus DC, Deutschman CS, Machado FR, Rubenfeld GD, Webb SA, Beale RJ, Vincent JL, Moreno R. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013 Feb;41(2):580–637. - PubMed
-
- Josefson P, Strålin K, Ohlin A, Ennefors T, Dragsten B, Andersson L, Fredlund H, Mölling P, Olcén P. Evaluation of a commercial multiplex PCR test (SeptiFast) in the etiological diagnosis of community-onset bloodstream infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011 Sep;30(9):1127–1134. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
