Identification of critical phosphorylation sites on the carboxy tail of melanopsin
- PMID: 24678795
- PMCID: PMC4010260
- DOI: 10.1021/bi401724r
Identification of critical phosphorylation sites on the carboxy tail of melanopsin
Abstract
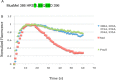
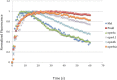
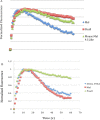
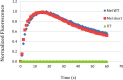
Light-activated opsins undergo carboxy-terminal phosphorylation, which contributes to the deactivation of their photoresponse. The photopigment melanopsin possesses an unusually long carboxy tail containing 37 serine and threonine sites that are potential sites for phosphorylation by a G-protein dependent kinase (GRK). Here, we show that a small cluster of six to seven sites is sufficient for deactivation of light-activated mouse melanopsin. Surprisingly, these sites are distinct from those that regulate deactivation of rhodopsin. In zebrafish, there are five different melanopsin genes that encode proteins with distinct carboxy-terminal domains. Naturally occurring changes in the same cluster of phosphorylatable amino acids provides diversity in the deactivation kinetics of the zebrafish proteins. These results suggest that variation in phosphorylation sites provides flexibility in the duration and kinetics of melanopsin-mediated light responses.
Figures




References
-
- Panda S.; Provencio I.; Tu D. C.; Pires S. S.; Rollag M. D.; Castrucci A. M.; Pletcher M. T.; Sato T. K.; Wiltshire T.; Andahazy M.; Kay S. A.; Van Gelder R. N.; Hogenesch J. B. (2003) Melanopsin is required for non-image-forming photic responses in blind mice. Science 301, 525–527. - PubMed
-
- Lucas R. J.; Hattar S.; Takao M.; Berson D. M.; Foster R. G.; Yau K. W. (2003) Diminished pupillary light reflex at high irradiances in melanopsin-knockout mice. Science 299, 245–247. - PubMed
-
- Tsai J. W.; Hannibal J.; Hagiwara G.; Colas D.; Ruppert E.; Ruby N. F.; Heller H. C.; Franken P.; Bourgin P. (2009) Melanopsin as a sleep modulator: Circadian gating of the direct effects of light on sleep and altered sleep homeostasis in Opn4–/– mice. PLoS Biol. 7, e1000125-1–e1000125-12. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

