Cellular communication and heterogeneity in pancreatic islet insulin secretion dynamics
- PMID: 24679927
- PMCID: PMC4112137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2014.02.005
Cellular communication and heterogeneity in pancreatic islet insulin secretion dynamics
Abstract
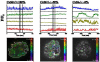
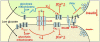
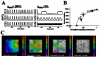
Coordinated pulses of electrical activity and insulin secretion are a hallmark of the islet of Langerhans. These coordinated behaviors are lost when β cells are dissociated, which also leads to increased insulin secretion at low glucose levels. Islets without gap junctions exhibit asynchronous electrical activity similar to dispersed cells, but their secretion at low glucose levels is still clamped off, putatively by a juxtacrine mechanism. Mice lacking β cell gap junctions have near-normal average insulin levels, but are glucose intolerant due to reduced first-phase and pulsatile insulin secretion, illustrating the importance of temporal dynamics. Here, we review the quantitative data on islet synchronization and the current mathematical models that have been developed to explain these behaviors and generate greater understanding of the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: calcium waves; computer modeling; fluorescence; islet of Langerhans; microscopy.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
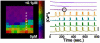
References
-
- Pipeleers D. The biosociology of pancreatic b cells. Diabetologia. 1987;30(5):277–291. - PubMed
-
- Pipeleers D, Kiekens R, Ling Z, Wilikens A, Schuit F. Physiologic relevance of heterogeneity in the pancreatic beta-cell population. Diabetologia. 1994;37(Suppl 2):S57–64. - PubMed
-
- Song SH, Kjems L, Ritzel R, McIntyre SM, Johnson ML, Veldhuis JD, Butler PC. Pulsatile insulin secretion by human pancreatic islets. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002;87(1):213–221. - PubMed
-
- Bergsten P. Slow and fast oscillations of cytoplasmic ca2+ in pancreatic islets correspond to pulsatile insulin release. Am. J. Physiol. Endo. Metab. 1995;268(2 Pt 1):E282–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK085064/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD016216/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- DK053434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK085145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025649/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK085145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK085145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK98659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK098659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085064/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD010681/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK058212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR026828/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

