Label-free in vivo imaging of myelinated axons in health and disease with spectral confocal reflectance microscopy
- PMID: 24681598
- PMCID: PMC3981936
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3495
Label-free in vivo imaging of myelinated axons in health and disease with spectral confocal reflectance microscopy
Abstract
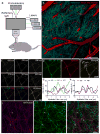
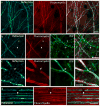
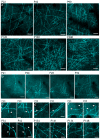
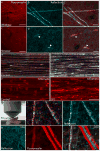
We report a newly developed technique for high-resolution in vivo imaging of myelinated axons in the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerve that requires no fluorescent labeling. This method, based on spectral confocal reflectance microscopy (SCoRe), uses a conventional laser-scanning confocal system to generate images by merging the simultaneously reflected signals from multiple lasers of different wavelengths. Striking color patterns unique to individual myelinated fibers are generated that facilitate their tracing in dense axonal areas. These patterns highlight nodes of Ranvier and Schmidt-Lanterman incisures and can be used to detect various myelin pathologies. Using SCoRe we carried out chronic brain imaging up to 400 μm deep, capturing de novo myelination of mouse cortical axons in vivo. We also established the feasibility of imaging myelinated axons in the human cerebral cortex. SCoRe adds a powerful component to the evolving toolbox for imaging myelination in living animals and potentially in humans.
Figures

References
-
- Nave KA. Myelination and support of axonal integrity by glia. Nature. 2010;468:244–52. - PubMed
-
- Franklin RJM, Ffrench-Constant C. Remyelination in the CNS: from biology to therapy. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:839–55. - PubMed
-
- Fancy SPJ, Chan JR, Baranzini SE, Franklin RJM, Rowitch DH. Myelin regeneration: a recapitulation of development? Annu Rev Neurosci. 2011;34:21–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

