Meta-analysis of infectious agents and depression
- PMID: 24681753
- PMCID: PMC5380112
- DOI: 10.1038/srep04530
Meta-analysis of infectious agents and depression
Abstract
Depression is a debilitating psychiatric disorder and a growing global public health issue. However, the relationships between microbial infections and depression remains uncertain. A computerized literature search of Medline, ISI Web of Knowledge, PsycINFO, and the Cochrane Library was conducted up to May 2013, and 6362 studies were initially identified for screening. Case-control studies detected biomarker of microorganism were included. Based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, 28 studies were finally included to compare the detection of 16 infectious agents in unipolar depressed patients and healthy controls with a positive incident being defined as a positive biochemical marker of microbial infection. A customized form was used for data extraction. Pooled analysis revealed that the majority of the 16 infectious agents were not significantly associated with depression. However, there were statistically significant associations between depression and infection with Borna disease virus, herpes simplex virus-1, varicella zoster virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and Chlamydophila trachomatis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




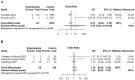
References
-
- Ustun T. B. et al. Multiple-informant ranking of the disabling effects of different health conditions in 14 countries. WHO/NIH Joint Project CAR Study Group. Lancet 354, 111–115 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Murray C. J. & Lopez A. D. Evidence-based health policy--lessons from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Science (New York, N.Y.) 274, 740–743 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Nestler E. J. et al. Neurobiology of depression. Neuron 34, 13–25 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Brooks-Gunn J. & Duncan G. J. The effects of poverty on children. The future of children, 55–71 (1997). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

