Decreased mitochondrial priming determines chemoresistance of colon cancer stem cells
- PMID: 24682005
- PMCID: PMC4207483
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.37
Decreased mitochondrial priming determines chemoresistance of colon cancer stem cells
Abstract
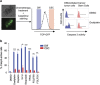
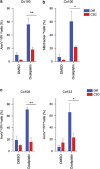
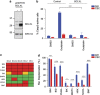
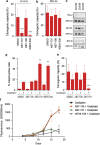
Tumor heterogeneity is in part determined by the existence of cancer stem cells (CSCs) and more differentiated tumor cells. CSCs are considered to be the tumorigenic root of cancers and suggested to be chemotherapy resistant. Here we exploited an assay that allowed us to measure chemotherapy-induced cell death in CSCs and differentiated tumor cells simultaneously. This confirmed that CSCs are selectively resistant to conventional chemotherapy, which we revealed is determined by decreased mitochondrial priming. In agreement, lowering the anti-apoptotic threshold using ABT-737 and WEHI-539 was sufficient to enhance chemotherapy efficacy, whereas ABT-199 failed to sensitize CSCs. Our data therefore point to a crucial role of BCLXL in protecting CSCs from chemotherapy and suggest that BH3 mimetics, in combination with chemotherapy, can be an efficient way to target chemotherapy-resistant CSCs.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, Nordlinger B, Cervantes A, Group EGW Advanced colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for treatment. Ann Oncol. 2010;21 (Suppl 5:v93–v97. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. New Engl J Med. 2004;351:337–345. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. New Engl J Med. 2004;350:2335–2342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

