Conditioned media from mesenchymal stromal cells restore sodium transport and preserve epithelial permeability in an in vitro model of acute alveolar injury
- PMID: 24682451
- PMCID: PMC4042188
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00242.2013
Conditioned media from mesenchymal stromal cells restore sodium transport and preserve epithelial permeability in an in vitro model of acute alveolar injury
Abstract
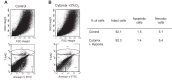
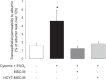
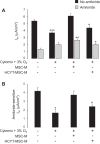
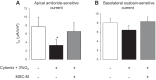
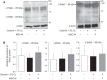
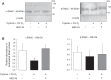
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) or their media (MSC-M) were reported to reverse acute lung injury (ALI)-induced decrease of alveolar fluid clearance. To determine the mechanisms by which MSC-M exert their beneficial effects, an in vitro model of alveolar epithelial injury was created by exposing primary rat alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) to hypoxia (3% O2) plus cytomix, a combination of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ. MSC-M were collected from human MSCs exposed for 12 h to either normoxia (MSC-M) or to hypoxia plus cytomix (HCYT-MSC-M). This latter condition was used to model the effect of alveolar inflammation and hypoxia on paracrine secretion of MSCs in the injured lung. Comparison of paracrine soluble factors in MSC media showed that the IL-1 receptor antagonist and prostaglandin E2 were markedly increased while keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) was twofold lower in HCYT-MSC-M compared with MSC-M. In AECs, hypoxia plus cytomix increased protein permeability, reduced amiloride-sensitive short-circuit current (AS-Isc), and also decreased the number of α-epithelial sodium channel (α-ENaC) subunits in the apical membrane. To test the effects of MSC media, MSC-M and HCYT-MSC-M were added for an additional 12 h to AECs exposed to hypoxia plus cytomix. MSC-M and HCYT-MSC-M completely restored epithelial permeability to normal. MSC-M, but not HCYT-MSC-M, significantly prevented the hypoxia plus cytomix-induced decrease of ENaC activity and restored apical α-ENaC channels. Interestingly, KGF-deprived MSC-M were unable to restore amiloride-sensitive sodium transport, indicating a possible role for KGF in the beneficial effect of MSC-M. These results indicate that MSC-M may be a preferable therapeutic option for ALI.
Keywords: growth factors; hypoxia; inflammation; membrane transport; mesenchymal stem cells; sodium channels.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Abreu SC, Antunes MA, Pelosi P, Morales MM, Rocco PR. Mechanisms of cellular therapy in respiratory diseases. Intensive Care Med 37: 1421–1431, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Amariglio N, Hirshberg A, Scheithauer BW, Cohen Y, Loewenthal R, Trakhtenbrot L, Paz N, Koren-Michowitz M, Waldman D, Leider-Trejo L, Toren A, Constantini S, Rechavi G. Donor-derived brain tumor following neural stem cell transplantation in an ataxia telangiectasia patient. PLoS Med 6: e1000029, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnulf B, Lecourt S, Soulier J, Ternaux B, Lacassagne MN, Crinquette A, Dessoly J, Sciaini AK, Benbunan M, Chomienne C, Fermand JP, Marolleau JP, Larghero J. Phenotypic and functional characterization of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived from patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia 21: 158–163, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Berthiaume Y, Folkesson HG, Matthay MA. Indomethacin does not influence alveolar liquid clearance in anesthetized sheep or rats. Exp Lung Res 25: 517–530, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

