On the discovery and development of pimavanserin: a novel drug candidate for Parkinson's psychosis
- PMID: 24682754
- PMCID: PMC4172996
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-014-1293-3
On the discovery and development of pimavanserin: a novel drug candidate for Parkinson's psychosis
Abstract
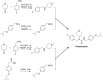
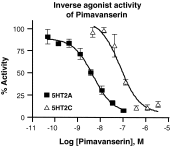
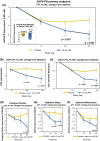
Parkinson's disease psychosis (PDP) is a condition that may develop in up to 60 % of Parkinson's patients, and is a major reason for nursing home placement for those affected. There are no FDA approved drugs for PDP but low doses of atypical anti-psychotic drugs (APDs) are commonly prescribed off-label. Only low-dose clozapine has shown efficacy in randomized controlled trials, but all APDs have black box warnings related to the increased mortality and morbidity when used in elderly demented patients. Using molecular pharmacological profiling of a large collection of marketed drugs, we discovered that potent inverse agonist activity against 5-HT2A serotonin receptors was a common feature of atypical APDs, especially the atypical APDs used to treat PDP. Since low-dose clozapine therapy selectively blocks this receptor, it was hypothesized that a highly selective 5-HT2A receptor inverse agonist might provide good symptom control in patients suffering from PDP, with a greatly improved safety and tolerability profile. A high throughput screening and subsequent chemical lead optimization campaign to develop potent, selective 5-HT2A receptor inverse agonists was launched, eventually resulting in the discovery of pimavanserin. Pimavanserin displays nanomolar potency as a 5-HT2A receptor inverse agonist, selectivity for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2C receptors, and no meaningful activity at any other G-protein coupled receptor. It demonstrated robust activity in preclinical models of schizophrenia and PDP, and did not worsen motoric symptoms, in contrast to the APDs tested. In a Phase III clinical trial, pimavanserin showed highly significant benefits in the primary endpoint, the scale for assessment of positive symptoms-PD, a scale adapted for use in PDP. In addition, improvements in all other efficacy endpoints, including physician's clinical global impression, caregiver burden, night-time sleep quality and daytime wakefulness, were seen. Pimavanserin demonstrated good safety and tolerability and did not worsen motoric symptoms as assessed by the unified Parkinson's disease rating scale parts II and III. An open-label extension study has further demonstrated that pimavanserin is safe and well-tolerated with long-term use. Pimavanserin may therefore offer a viable treatment option for patients suffering from PDP.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

