The efficacy of ticagrelor is maintained in women with acute coronary syndromes participating in the prospective, randomized, PLATelet inhibition and patient Outcomes (PLATO) trial
- PMID: 24682844
- PMCID: PMC4057642
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu075
The efficacy of ticagrelor is maintained in women with acute coronary syndromes participating in the prospective, randomized, PLATelet inhibition and patient Outcomes (PLATO) trial
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study was to assess the relationship between sex and clinical outcomes and treatment-related complications in patients with ST-elevation or non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes (ACS) randomized to treatment with ticagrelor or clopidogrel in the PLATelet inhibition and patient Outcomes (PLATO) trial.
Methods: The associations between sex subgroup and the primary composite outcomes, secondary outcomes, and major bleeding endpoints as well as interaction of sex subgroup with treatment effects were analysed using Cox proportional-hazards models.
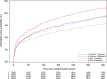
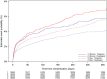
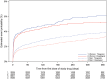
Results: Sex was not significantly associated with the probability of the primary composite endpoint [adjusted hazard ratio (HR): 1.02 (0.91-1.16)], or other adverse cardiovascular endpoints. Ticagrelor was similarly more effective than clopidogrel in reducing rates of the primary endpoint in women 11.2 vs. 13.2% [adjusted HR: 0.88 (0.74-1.06)] and men 9.4 vs. 11.1% [adjusted HR: 0.86 (0.76-0.97)] (interaction P-value 0.78), all-cause death in women 5.8 vs. 6.8% [adjusted HR: 0.90 (0.69-1.16)] and men 4.0 vs. 5.7% [adjusted HR: 0.80 (0.67-0.96)] (interaction P-value 0.49), and definite stent thrombosis in women 1.2 vs. 1.4% [adjusted HR: 0.71 (0.36-1.38)] and men 1.4 vs. 2.1% [adjusted HR: 0.63 (0.45-0.89)] (interaction P-value 0.78). The treatments did not differ for PLATO-defined overall major bleeding complications in women [adjusted HR: 1.01 (0.83-1.23)] or men [adjusted HR: 1.10 (0.98-1.24)]. Sex had no significant association with these outcomes (interactions P = 0.43-0.88).
Conclusion: Female sex is not an independent risk factor for adverse clinical outcomes in moderate-to-high risk ACS patients. Ticagrelor has a similar efficacy and safety profile in men and women.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00391872.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndromes; P2Y12 receptor; Platelets; Sex; Thrombosis; Ticagrelor.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


References
-
- Maynard C, Every NR, Martin JS, Kudenchuk PJ, Weaver WD. Association of gender and survival in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:1379–1384. - PubMed
-
- Moen EK, Asher CR, Miller DP, Weaver WD, White HD, Califf RM, Topol EJ. Long-term follow-up of gender-specific outcomes after thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction from the GUSTO-I trial. Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries. J Womens Health. 1997;6:285–293. - PubMed
-
- Chandra NC, Ziegelstein RC, Rogers WJ, Tiefenbrunn AJ, Gore JM, French WJ, Rubison M. Observations of the treatment of women in the United States with myocardial infarction: a report from the National Registry of Myocardial Infarction-I. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158:981–988. - PubMed
-
- Hochman JS, Tamis JE, Thompson TD, Weaver WD, White HD, Van de Werf F, Aylward P, Topol EJ, Califf RM. Sex, clinical presentation, and outcome in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Global Use of Strategies to Open Occluded Coronary Arteries in Acute Coronary Syndromes IIb Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:226–232. - PubMed
-
- Gan SC, Beaver SK, Houck PM, MacLehose RF, Lawson HW, Chan L. Treatment of acute myocardial infarction and 30-day mortality among women and men. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:8–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

