Refractory pancolitis: a novel presentation of idiopathic myointimal hyperplasia of mesenteric veins
- PMID: 24683381
- PMCID: PMC3969016
Refractory pancolitis: a novel presentation of idiopathic myointimal hyperplasia of mesenteric veins
Figures
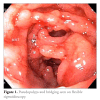
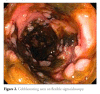
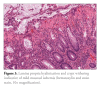
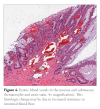


References
-
- Kornbluth A, Sachar DB. Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults (update): American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:1371–1385. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz DA, Loftus EV, Jr, Tremaine WJ, et al. The natural history of fistulizing Crohn’s disease in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:875–880. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein GR, Hanauer SB, Sandborn WJ. Practice Parameters Committee of American College of Gastroenterology. Management of Crohn’s disease in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:465–483. quiz 464, 484. - PubMed
-
- Genta RM, Haggitt RC. Idiopathic myointimal hyperplasia of mesenteric veins. Gastroenterology. 1991;101:533–539. - PubMed
-
- Kao PC, Vecchio JA, Hyman NH, West AB, Blaszyk H. Idiopathic myointimal hyperplasia of mesenteric veins: a rare mimic of idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39:704–708. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
