IGF-I regulates redox status in breast cancer cells by activating the amino acid transport molecule xC-
- PMID: 24686172
- PMCID: PMC4006361
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1803
IGF-I regulates redox status in breast cancer cells by activating the amino acid transport molecule xC-
Abstract
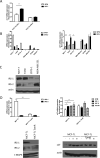
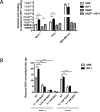
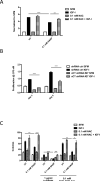
Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) stimulate cell growth in part by increasing amino acid uptake. xCT (SLC7A11) encodes the functional subunit of the cell surface transport system xC(-), which mediates cystine uptake, a pivotal step in glutathione synthesis and cellular redox control. In this study, we show that IGF-I regulates cystine uptake and cellular redox status by activating the expression and function of xCT in estrogen receptor-positive (ER(+)) breast cancer cells by a mechanism that relies on the IGF receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Breast cancer cell proliferation mediated by IGF-I was suppressed by attenuating xCT expression or blocking xCT activity with the pharmacologic inhibitor sulfasalazine (SASP). Notably, SASP sensitized breast cancer cells to inhibitors of the type I IGF receptor (IGF-IR) in a manner reversed by the reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger N-acetyl-L-cysteine. Thus, IGF-I promoted the proliferation of ER(+) breast cancer cells by regulating xC(-) transporter function to protect cancer cells from ROS in an IRS-1-dependent manner. Our findings suggest that inhibiting xC(-) transporter function may synergize with modalities that target the IGF-IR to heighten their therapeutic effects.
©2014 AACR.
Figures



References
-
- Sachdev D, Yee D. The IGF system and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2001;8:197–209. - PubMed
-
- Pollak M. The insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: an update. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:159–69. - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B, Kahn CR. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2006;7:85–96. - PubMed
-
- Jackson JG, White MF, Yee D. Insulin receptor substrate-1 is the predominant signaling molecule activated by insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin, and interleukin-4 in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:9994–10003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

