High fat diet produces brain insulin resistance, synaptodendritic abnormalities and altered behavior in mice
- PMID: 24686304
- PMCID: PMC4083060
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.03.011
High fat diet produces brain insulin resistance, synaptodendritic abnormalities and altered behavior in mice
Abstract
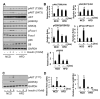
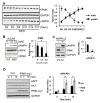
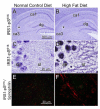
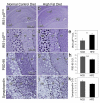
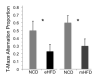
Insulin resistance and other features of the metabolic syndrome are increasingly recognized for their effects on cognitive health. To ascertain mechanisms by which this occurs, we fed mice a very high fat diet (60% kcal by fat) for 17days or a moderate high fat diet (HFD, 45% kcal by fat) for 8weeks and examined changes in brain insulin signaling responses, hippocampal synaptodendritic protein expression, and spatial working memory. Compared to normal control diet mice, cerebral cortex tissues of HFD mice were insulin-resistant as evidenced by failed activation of Akt, S6 and GSK3β with ex-vivo insulin stimulation. Importantly, we found that expression of brain IPMK, which is necessary for mTOR/Akt signaling, remained decreased in HFD mice upon activation of AMPK. HFD mouse hippocampus exhibited increased expression of serine-phosphorylated insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1-pS(616)), a marker of insulin resistance, as well as decreased expression of PSD-95, a scaffolding protein enriched in post-synaptic densities, and synaptopodin, an actin-associated protein enriched in spine apparatuses. Spatial working memory was impaired as assessed by decreased spontaneous alternation in a T-maze. These findings indicate that HFD is associated with telencephalic insulin resistance and deleterious effects on synaptic integrity and cognitive behaviors.
Keywords: Akt; GSK3; IPMK; Insulin; Insulin receptor substrate 1; Spine; Synapse; Working memory; mTOR.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Amato L, et al. The Osservatorio Geriatrico of Campania Region Group Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is associated with a greater prevalence of depression in the elderly. Diabetes Metab. 1996;22:314–8. - PubMed
-
- Artola A, et al. Diabetes mellitus concomitantly facilitates the induction of long-term depression and inhibits that of long-term potentiation in hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;22:169–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

