Structure activity relationship of brevenal hydrazide derivatives
- PMID: 24686558
- PMCID: PMC4012454
- DOI: 10.3390/md12041839
Structure activity relationship of brevenal hydrazide derivatives
Abstract
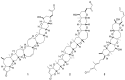
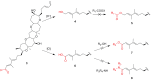
Brevenal is a ladder frame polyether produced by the dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. This organism is also responsible for the production of the neurotoxic compounds known as brevetoxins. Ingestion or inhalation of the brevetoxins leads to adverse effects such as gastrointestinal maladies and bronchoconstriction. Brevenal shows antagonistic behavior to the brevetoxins and shows beneficial attributes when administered alone. For example, in an asthmatic sheep model, brevenal has been shown to increase tracheal mucosal velocity, an attribute which has led to its development as a potential treatment for Cystic Fibrosis. The mechanism of action of brevenal is poorly understood and the exact binding site has not been elucidated. In an attempt to further understand the mechanism of action of brevenal and potentially develop a second generation drug candidate, a series of brevenal derivatives were prepared through modification of the aldehyde moiety. These derivatives include aliphatic, aromatic and heteroaromatic hydrazide derivatives. The brevenal derivatives were tested using in vitro synaptosome binding assays to determine the ability of the compounds to displace brevetoxin and brevenal from their native receptors. A sheep inhalation model was used to determine if instillation of the brevenal derivatives resulted in bronchoconstriction. Only small modifications were tolerated, with larger moieties leading to loss of affinity for the brevenal receptor and bronchoconstriction in the sheep model.
Figures

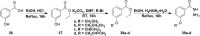


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

