Speech sound production in 2-year-olds who are hard of hearing
- PMID: 24686852
- PMCID: PMC4035418
- DOI: 10.1044/2014_AJSLP-13-0039
Speech sound production in 2-year-olds who are hard of hearing
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of the study was to (a) compare the speech sound production abilities of 2-year-old children who are hard of hearing (HH) to children with normal hearing (NH), (b) identify sources of risk for individual children who are HH, and (c) determine whether speech sound production skills at age 2 were predictive of speech sound production skills at age 3.
Method: Seventy children with bilateral, mild-to-severe hearing loss who use hearing aids and 37 age- and socioeconomic status-matched children with NH participated. Children's speech sound production abilities were assessed at 2 and 3 years of age.
Results: At age 2, the HH group demonstrated vowel production abilities on par with their NH peers but weaker consonant production abilities. Within the HH group, better outcomes were associated with hearing aid fittings by 6 months of age, hearing loss of less than 45 dB HL, stronger vocabulary scores, and being female. Positive relationships existed between children's speech sound production abilities at 2 and 3 years of age.
Conclusion: Assessment of early speech sound production abilities in combination with demographic, audiologic, and linguistic variables may be useful in identifying HH children who are at risk for delays in speech sound production.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
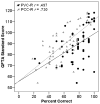
Figures

References
-
- ANSI. Technical Report S3.5-1997. New York: American National Standards Institute; 1997. Methods for calculation of the speech intelligibility index.
-
- Bentler R, Hu YH, Cole B. Deriving an audibility index for frequency-lowered hearing aids. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Auditory Society; Scottsdale, AZ. 2011. Mar,
-
- Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

