Functionally distinct PI 3-kinase pathways regulate myelination in the peripheral nervous system
- PMID: 24687281
- PMCID: PMC3971744
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201307057
Functionally distinct PI 3-kinase pathways regulate myelination in the peripheral nervous system
Abstract
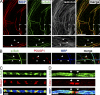
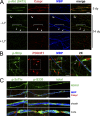
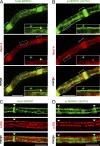
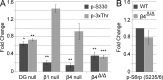
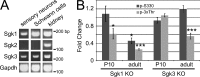
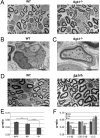
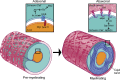
The PI 3-kinase (PI 3-K) signaling pathway is essential for Schwann cell myelination. Here we have characterized PI 3-K effectors activated during myelination by probing myelinating cultures and developing nerves with an antibody that recognizes phosphorylated substrates for this pathway. We identified a discrete number of phospho-proteins including the S6 ribosomal protein (S6rp), which is down-regulated at the onset of myelination, and N-myc downstream-regulated gene-1 (NDRG1), which is up-regulated strikingly with myelination. We show that type III Neuregulin1 on the axon is the primary activator of S6rp, an effector of mTORC1. In contrast, laminin-2 in the extracellular matrix (ECM), signaling through the α6β4 integrin and Sgk1 (serum and glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1), drives phosphorylation of NDRG1 in the Cajal bands of the abaxonal compartment. Unexpectedly, mice deficient in α6β4 integrin signaling or Sgk1 exhibit hypermyelination during development. These results identify functionally and spatially distinct PI 3-K pathways: an early, pro-myelinating pathway driven by axonal Neuregulin1 and a later-acting, laminin-integrin-dependent pathway that negatively regulates myelination.
Figures



References
-
- Alessi D.R., Deak M., Casamayor A., Caudwell F.B., Morrice N., Norman D.G., Gaffney P., Reese C.B., MacDougall C.N., Harbison D., et al. 1997a. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1): structural and functional homology with the Drosophila DSTPK61 kinase. Curr. Biol. 7:776–789 10.1016/S0960-9822(06)00336-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Atanasoski S., Scherer S.S., Sirkowski E., Leone D., Garratt A.N., Birchmeier C., Suter U. 2006. ErbB2 signaling in Schwann cells is mostly dispensable for maintenance of myelinated peripheral nerves and proliferation of adult Schwann cells after injury. J. Neurosci. 26:2124–2131 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4594-05.2006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

