Selective digestive or oropharyngeal decontamination and topical oropharyngeal chlorhexidine for prevention of death in general intensive care: systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 24687313
- PMCID: PMC3970764
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.g2197
Selective digestive or oropharyngeal decontamination and topical oropharyngeal chlorhexidine for prevention of death in general intensive care: systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the effect on mortality of selective digestive decontamination, selective oropharyngeal decontamination, and topical oropharyngeal chlorhexidine in adult patients in general intensive care units and to compare these interventions with each other in a network meta-analysis.
Design: Systematic review, conventional meta-analysis, and network meta-analysis. Medline, Embase, and CENTRAL were searched to December 2012. Previous meta-analyses, conference abstracts, and key journals were also searched. We used pairwise meta-analyses to estimate direct evidence from intervention-control trials and a network meta-analysis within a Bayesian framework to combine direct and indirect evidence.
Inclusion criteria: Prospective randomised controlled trials that recruited adult patients in general intensive care units and studied selective digestive decontamination, selective oropharyngeal decontamination, or oropharyngeal chlorhexidine compared with standard care or placebo.
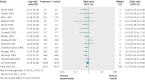
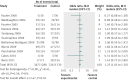
Results: Selective digestive decontamination had a favourable effect on mortality, with a direct evidence odds ratio of 0.73 (95% confidence interval 0.64 to 0.84). The direct evidence odds ratio for selective oropharyngeal decontamination was 0.85 (0.74 to 0.97). Chlorhexidine was associated with increased mortality (odds ratio 1.25, 1.05 to 1.50). When each intervention was compared with the other, both selective digestive decontamination and selective oropharyngeal decontamination were superior to chlorhexidine. The difference between selective digestive decontamination and selective oropharyngeal decontamination was uncertain.
Conclusion: Selective digestive decontamination has a favourable effect on mortality in adult patients in general intensive care units. In these patients, the effect of selective oropharyngeal decontamination is less certain. Both selective digestive decontamination and selective oropharyngeal decontamination are superior to chlorhexidine, and there is a possibility that chlorhexidine is associated with increased mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures


Comment in
-
[Intensive care: mouth rinse with chlorhexidine or antibiotic prophylaxis? Widespread application of chlorhexidine should be critically scrutinized].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2014 May;139(19):980. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1353903. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2014. PMID: 24782149 German. No abstract available.
-
ACP Journal Club. Review: Selective digestive decontamination reduces mortality more than chlorhexidine in general ICU patients.Ann Intern Med. 2014 Aug 19;161(4):JC9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-161-4-201408190-02009. Ann Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 25133388 No abstract available.
References
-
- Johanson WG, Pierce AK, Sanford JP, Thomas GD. Nosocomial respiratory infections with Gram-negative bacilli: the significance of colonization of the respiratory tract. Ann Int Med 1972;77:701-6. - PubMed
-
- Garrouste-Orgeas M, Chevret S, Arlet G, Marie O, Rouveau M, Popoff N, et al. Oropharyngeal or gastric colonization and nosocomial pneumonia in adult intensive care unit patients a prospective study based on genomic DNA analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997;156:1647-55. - PubMed
-
- De Smet A-M, Bonten MJ, Kluytmans JA. For whom should we use selective decontamination of the digestive tract? Curr Opin Infect Dis 2012;25:211-7. - PubMed
-
- Bonten MJ Brun-Buisson C, Weinstein RA. Selective decontamination of the digestive tract: to stimulate or stifle. Intensive Care Med 2003;29:672-6. - PubMed
-
- Van Saene HK, Petros AJ, Ramsay G, Baxby D. All great truths are iconoclastic: selective decontamination of the digestive tract moves from heresy to level 1 truth. Intensive Care Med 2003;29:677-90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
