In vitro and in vivo activities of HPi1, a selective antimicrobial against Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 24687512
- PMCID: PMC4068456
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02573-13
In vitro and in vivo activities of HPi1, a selective antimicrobial against Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
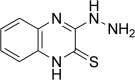
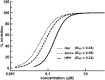
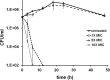
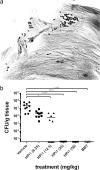
A high-throughput screen (HTS) was performed to identify molecules specifically active against Helicobacter pylori, the causative agent of peptic ulcer and gastric carcinoma. Currently, treatment of H. pylori infection is suboptimal, with failure rates approaching 25%, despite triple therapy with two broad-spectrum antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor or quadruple therapy with added bismuth. The HTS was performed in 384-well plates, and reduction of the metabolic indicator resazurin was used as a reporter for cell growth. Diverse molecules from commercial sources were identified as hits, and in vitro validations included measurements of MIC and time-dependent killing as well as anaerobic susceptibility testing against a panel of gut microbes. In vivo validation included testing in the mouse model of H. pylori infection. The small molecule HPi1 (3-hydrazinoquinoxaline-2-thiol) had excellent potency, with an MIC of 0.08 to 0.16 μg/ml and good selectivity for H. pylori compared to a panel of commensal bacteria. HPi1 was also effective in a mouse model of H. pylori infection, reducing colony counts to below the limit of detection after oral dosing of 25 mg/kg/day for 3 days. HPi1 is a promising lead in the search for more effective and specific H. pylori therapeutics.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Compare D, Rocco A, Nardone G. 2010. Risk factors in gastric cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 14:302–308 http://www.europeanreview.org/wp/wp-content/uploads/741.pdf - PubMed
-
- Lacy BE, Rosemore J. 2001. Helicobacter pylori: ulcers and more: the beginning of an era. J. Nutr. 131:2789S–2793S http://jn.nutrition.org/content/131/10/2789S.long - PubMed
-
- Luther J, Higgins PD, Schoenfeld PS, Moayyedi P, Vakil N, Chey WD. 2010. Empiric quadruple vs. triple therapy for primary treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and tolerability. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 105:65–73. 10.1038/ajg.2009.508 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pilotto A, Franceschi M, Rassu M, Leandro G, Bozzola L, Furlan F, Di Mario F. 2000. Incidence of secondary Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics in treatment failures after 1-week proton pump inhibitor-based triple therapies: a prospective study. Dig. Liver Dis. 32:667–672. 10.1016/S1590-8658(00)80327-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

