Polycystins and partners: proposed role in mechanosensitivity
- PMID: 24687583
- PMCID: PMC4080931
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.271346
Polycystins and partners: proposed role in mechanosensitivity
Abstract
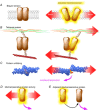
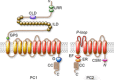
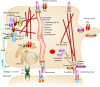
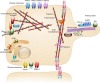
Mutations of the two polycystins, PC1 and PC2, lead to polycystic kidney disease. Polycystins are able to form complexes with numerous families of proteins that have been suggested to participate in mechanical sensing. The proposed role of polycystins and their partners in the kidney primary cilium is to sense urine flow. A role for polycystins in mechanosensing has also been shown in other cell types such as vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac myocytes. At the plasma membrane, polycystins interact with diverse ion channels of the TRP family and with stretch-activated channels (Piezos, TREKs). The actin cytoskeleton and its interacting proteins, such as filamin A, have been shown to be essential for these interactions. Numerous proteins involved in cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix junctions interact with PC1 and/or PC2. These multimeric protein complexes are important for cell structure integrity, the transmission of force, as well as for mechanosensing and mechanotransduction. A group of polycystin partners are also involved in subcellular trafficking mechanisms. Finally, PC1 and especially PC2 interact with elements of the endoplasmic reticulum and are essential components of calcium homeostasis. In conclusion, we propose that both PC1 and PC2 act as conductors to tune the overall cellular mechanosensitivity.
© 2014 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2014 The Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Alenghat FJ, Nauli SM, Kolb R, Zhou J, Ingber DE. Global cytoskeletal control of mechanotransduction in kidney epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 2004;301:23–30. - PubMed
-
- Arnadottir J, Chalfie M. Eukaryotic mechanosensitive channels. Annu Rev Biophys. 2010;39:111–137. - PubMed
-
- Arnould T, Kim E, Tsiokas L, Jochimsen F, Grüning W, Chang JD, Walz G. The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene product mediates protein kinase C α–dependent and c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent activation of the transcription factor AP 1. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:6013–6018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

