Zoledronic acid has differential antitumor activity in the pre- and postmenopausal bone microenvironment in vivo
- PMID: 24687923
- PMCID: PMC4040234
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1246
Zoledronic acid has differential antitumor activity in the pre- and postmenopausal bone microenvironment in vivo
Abstract
Purpose: Clinical trials in early breast cancer have suggested that benefits of adjuvant bone-targeted treatments are restricted to women with established menopause. We developed models that mimic pre- and postmenopausal status to investigate effects of altered bone turnover on growth of disseminated breast tumor cells. Here, we report a differential antitumor effect of zoledronic acid (ZOL) in these two settings.
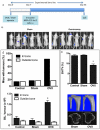
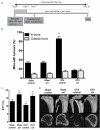
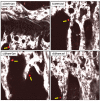
Experimental design: Twleve-week-old female Balb/c-nude mice with disseminated MDA-MB-231 breast tumor cells in bone underwent sham operation or ovariectomy (OVX), mimicking the pre- and postmenopausal bone microenvironment, respectively. To determine the effects of bone-targeted therapy, sham/OVX animals received saline or 100 μg/kg ZOL weekly. Tumor growth was assessed by in vivo imaging and effects on bone by real-time PCR, micro-CT, histomorphometry, and measurements of bone markers. Disseminated tumor cells were detected by two-photon microscopy.
Results: OVX increased bone resorption and induced growth of disseminated tumor cells in bone. Tumors were detected in 83% of animals following OVX (postmenopausal model) compared with 17% following sham operation (premenopausal model). OVX had no effect on tumors outside of bone. OVX-induced tumor growth was completely prevented by ZOL, despite the presence of disseminated tumor cells. ZOL did not affect tumor growth in bone in the sham-operated animals. ZOL increased bone volume in both groups.
Conclusions: This is the first demonstration that tumor growth is driven by osteoclast-mediated mechanisms in models that mimic post- but not premenopausal bone, providing a biologic rationale for the differential antitumor effects of ZOL reported in these settings. Clin Cancer Res; 20(11); 2922-32. ©2014 AACR.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


References
-
- Coleman RE, Marshall H, Cameron D, Dodwell D, Burkinshaw R, Keane M, et al. Breast cancer adjuvant therapy with zoledronic acid. New England Journal of Medicine. 2011;365:1396–405. - PubMed
-
- Paterson AHG, Anderson SJ, Lembersky BC, Fehrenbacher L, Falkson CI, King KM, et al. S2-3: NSABP Protocol B-34: A clinical trial comparing adjuvant clodronate vs. placebo in early stage breast cancer patients receiving systemic chemotherapy and/or tamoxifen or no therapy – final analysis. Cancer Research. 2011;71(24 Suppl 3):S2–3.
-
- Gnant M, Mlineritsch B, Stoeger H, Luschin-Ebengreuth G, Heck D, Menzel C, et al. Adjuvant endocrine therapy plus zoledronic acid in premenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer: 62-month follow-up from the ABCSG-12 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:631–41. - PubMed
-
- Townson JL, Chambers AF. Dormancy of solitary metastatic cells. Cell Cycle. 2006;16:1744–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

