Engagement of the ICOS pathway markedly enhances efficacy of CTLA-4 blockade in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 24687957
- PMCID: PMC3978270
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20130590
Engagement of the ICOS pathway markedly enhances efficacy of CTLA-4 blockade in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
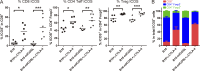
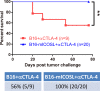
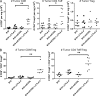
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) blockade with a monoclonal antibody yields durable responses in a subset of cancer patients and has been approved by the FDA as a standard therapy for late-stage melanoma. We recently identified inducible co-stimulator (ICOS) as a crucial player in the antitumor effects of CTLA-4 blockade. We now show that concomitant CTLA-4 blockade and ICOS engagement by tumor cell vaccines engineered to express ICOS ligand enhanced antitumor immune responses in both quantity and quality and significantly improved rejection of established melanoma and prostate cancer in mice. This study provides strong support for the development of combinatorial therapies incorporating anti-CTLA-4 and ICOS engagement.
Figures






References
-
- Carthon B.C., Wolchok J.D., Yuan J., Kamat A., Ng Tang D.S., Sun J., Ku G., Troncoso P., Logothetis C.J., Allison J.P., Sharma P. 2010. Preoperative CTLA-4 blockade: Tolerability and immune monitoring in the setting of a presurgical clinical trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 16:2861–2871 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0569 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Foster B.A., Gingrich J.R., Kwon E.D., Madias C., Greenberg N.M. 1997. Characterization of prostatic epithelial cell lines derived from transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) model. Cancer Res. 57:3325–3330 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

