Sex-specific association of the zinc finger protein 259 rs2075290 polymorphism and serum lipid levels
- PMID: 24688311
- PMCID: PMC3970100
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.8489
Sex-specific association of the zinc finger protein 259 rs2075290 polymorphism and serum lipid levels
Abstract
Background: Little is known about the association of ZNF259 rs2075290 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and serum lipid levels in the Chinese population. This study aimed to detect the association of ZNF259 rs2075290 SNP and environmental factors with serum lipid levels between males and females in the Mulao and Han populations.
Methods and results: Genotyping of ZNF259 rs2075290 SNP was performed in 788 of Mulao and 778 of Han participants using polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism. The genotype frequencies were significantly different between Mulao and Han populations (AA, 50.1% Vs 58.9%; AG, 42.3% Vs 35.7%; GG, 7.6% Vs 5.4%, P = 0.002) and between Han males and females (AA, 64.5% Vs 55.2%; AG, 28.3% Vs 40.6%; GG, 7.2% Vs 4.2%, P = 0.001). Serum levels of triglyceride (TG) in Mulao males, and total cholesterol (TC), TG and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in Mulao females were different between the AA and AG/GG genotypes (P < 0.05-0.001). Serum TC, LDL-C and apolipoprotein (Apo) A1 levels in Han males, and TG and ApoB levels and ApoA1/ApoB ratio in Han females were different between the AA and AG/GG genotypes (P < 0.05-0.001). An interaction between ZNF259 rs2075290 polymorphism and male gender on serum TC, LDL-C, and ApoA1 levels was noted in Han population (P < 0.05-0.01) but not in Mulao's.
Conclusions: The subjects with AG/GG genotype in Mulao males and females and Han females have less favorable lipid profiles than those with AA genotype. In contrast, the subjects with AG/GG genotype in Han males have more favorable lipid profiles than those with AA genotype. These findings suggest that the association between ZNF259 rs2075290 SNP and serum lipid levels might have ethnic- and/or sex-specificity.
Keywords: environmental factors.; lipids; sex-specific association; single nucleotide polymorphism; zinc finger protein 259 (ZNF259).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
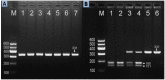
References
-
- Mittendorfer B. Sexual dimorphism in human lipid metabolism. J Nutr. 2005;135(4):681–686. - PubMed
-
- Cullen P. Evidence that triglycerides are an independent coronary heart disease risk factor. Am J Cardiol. 2000;86(9):943–949. - PubMed
-
- Meagher EA. Addressing cardiovascular disease in women: focus on dyslipidemia. J Am Board Fam Pract. 2004;17(6):424–437. - PubMed
-
- Teo YY, Sim X. Patterns of linkage disequilibrium in different populations: implications and opportunities for lipid-associated loci identified from genome-wide association studies. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2010;21(2):104–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

