Self-insight in probabilistic categorization - not implicit in children either
- PMID: 24688476
- PMCID: PMC3960589
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00233
Self-insight in probabilistic categorization - not implicit in children either
Abstract
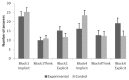
The weather prediction (WP) task is a probabilistic category learning task that was designed to be implicit/procedural. In line with this claim, early results showed that patients with amnesia perform comparably to healthy participants. On the other hand, later research on healthy adult participants drew attention to the fact that the WP task is not necessarily implicit. There have been results showing that participants can access structural information acquired during the task. Participants also report that their responses are based on memories and rule knowledge. The contradictory results may be reconciled by assuming that while explicit learning occurs on the WP task in case of adults, in children the learning process is implicit. The present study aims at testing this hypothesis. Primary school children completed the WP task; the experimental group performed the original task, whereas in the control group cues and outcomes were associated on a random basis, hence their version of the WP task lacked a predictive structure. After each item, participants were asked whether they relied on guessing, intuition, "I think I know the answer" type of knowledge, memories of previous items, or knowledge of rules. Self-insight reports of the experimental group were compared to a control group. Results showed that children learn similarly to adults: they mostly (but not completely) rely on explicit, and not on implicit processes.
Keywords: children; development; explicit learning; implicit learning; probabilistic categorization; self-insight; weather prediction task.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

