Cgl-SLT2 is required for appressorium formation, sporulation and pathogenicity in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides
- PMID: 24688518
- PMCID: PMC3958194
- DOI: 10.1590/s1517-83822013000400031
Cgl-SLT2 is required for appressorium formation, sporulation and pathogenicity in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides
Abstract
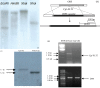
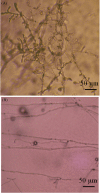
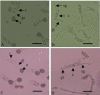
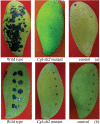
The mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways has been implicated in the pathogenicity of various pathogenic fungi and plays important roles in regulating pathogenicity-related morphogenesis. This work describes the isolation and characterization of MAP kinase gene, Cgl-SLT2, from Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. A DNA sequence, including 1,633 bp of Cgl-SLT2 open-reading frame and its promoter and terminator regions, was isolated via DNA walking and cloned. To analyze gene function, a gene disruption cassette containing hygromycin-resistant gene was constructed, and Cgl-SLT2 was inactivated via gene deletion. Analysis on Cgl-slt2 mutant revealed a defect in vegetative growth and sporulation as compared to the wild-type strain. When grown under nutrient-limiting conditions, hyperbranched hyphal morphology was observed in the mutant. Conidia induction for germination on rubber wax-coated hard surfaces revealed no differences in the percentage of conidial germination between the wild-type and Cgl-slt2 mutant. However, the percentage of appressorium formation in the mutant was greatly reduced. Bipolar germination in the mutant was higher than in the wild-type at 8-h post-induction. A pathogenicity assay revealed that the mutant was unable to infect either wounded or unwounded mangoes. These results suggest that the Cgl-SLT2 MAP kinase is required for C. gloeosporioides conidiation, polarized growth, appressorium formation and pathogenicity.
Keywords: Colletotrichum gloeosporioides; MAP kinase; appressorium; pathogenicity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade CgSte50-Ste11-Ste7-Mk1 regulates infection-related morphogenesis in the poplar anthracnose fungus Colletotrichum gloeosporioides.Microbiol Res. 2021 Jul;248:126748. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2021.126748. Epub 2021 Mar 14. Microbiol Res. 2021. PMID: 33752111
-
[Gene cloning and biological function of CgRGS2 in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2017 Jan 4;57(1):66-76. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 29746761 Chinese.
-
ABC protein CgABCF2 is required for asexual and sexual development, appressorial formation and plant infection in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides.Microb Pathog. 2017 Sep;110:85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.06.028. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28645773
-
Transcription factor CgAzf1 regulates melanin production, conidial development and infection in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2019 Jul;112(7):1095-1104. doi: 10.1007/s10482-019-01243-1. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2019. PMID: 30725325
-
The Colletotrichum lagenarium MAP kinase gene CMK1 regulates diverse aspects of fungal pathogenesis.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2000 Apr;13(4):374-83. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.4.374. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2000. PMID: 10755300
Cited by
-
Protein Kinase Signaling Pathways in Plant-Colletotrichum Interaction.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jan 20;12:829645. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.829645. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35126439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase CgMK1 Governs Appressorium Formation, Melanin Synthesis, and Plant Infection of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides.Front Microbiol. 2017 Nov 10;8:2216. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02216. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29176970 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid Synthase Beta Dehydratase in the Lipid Biosynthesis Pathway Is Required for Conidiogenesis, Pigmentation and Appressorium Formation in Magnaporthe oryzae S6.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 30;21(19):7224. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197224. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33007862 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of the Slt2 ortholog from Cryphonectria parasitica results in abnormal cell wall integrity and sectorization with impaired pathogenicity.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 22;7(1):9038. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09383-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28831166 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Conidiogenesis-Associated Genes in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation.Curr Microbiol. 2016 Dec;73(6):802-810. doi: 10.1007/s00284-016-1131-8. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Curr Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27582094
References
-
- Alic N, Higgins VJ, Pichova A, Breitenbach M, Dawes IW. Lipid hydroperoxides activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase Mpk1p in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(43):41849–41855. - PubMed
-
- Arauz LF. Mango anthracnose: economic impact and current options for integrated management. Plant Dis. 2000;84(6):600–611. - PubMed
-
- Barhoom S, Sharon A. cAMP regulation of “pathogenic” and “saprophytic” fungal spore germination. Fungal Genet Biol. 2004;41(3):317–326. - PubMed
-
- Di Pietro A, García-Maceira FI, Méglecz E, Roncero MIG. A MAP kinase of the vascular wilt fungus Fusarium oxysporum is essential for root penetration and pathogenesis. Mol Microbiol. 2001;39(5):1140–1152. - PubMed
-
- Ebbole DJ. Magnaporthe as a model for understanding host-pathogen interactions. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2007;45(1):437–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
