Statistical methods for the analysis of high-throughput metabolomics data
- PMID: 24688690
- PMCID: PMC3962125
- DOI: 10.5936/csbj.201301009
Statistical methods for the analysis of high-throughput metabolomics data
Abstract
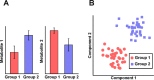
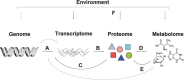
Metabolomics is a relatively new high-throughput technology that aims at measuring all endogenous metabolites within a biological sample in an unbiased fashion. The resulting metabolic profiles may be regarded as functional signatures of the physiological state, and have been shown to comprise effects of genetic regulation as well as environmental factors. This potential to connect genotypic to phenotypic information promises new insights and biomarkers for different research fields, including biomedical and pharmaceutical research. In the statistical analysis of metabolomics data, many techniques from other omics fields can be reused. However recently, a number of tools specific for metabolomics data have been developed as well. The focus of this mini review will be on recent advancements in the analysis of metabolomics data especially by utilizing Gaussian graphical models and independent component analysis.
Figures

References
-
- Oliver SG, Winson MK, Kell DB, Baganz F (1998) Systematic functional analysis of the yeast genome. Trends in Biotechnology 16: 373–378 - PubMed
-
- Ludwig C, Viant MR (2010) Two-dimensional J-resolved NMR spectroscopy: review of a key methodology in the metabolomics toolbox. Phytochem Anal 21: 22–32 - PubMed
-
- Roux A, Lison D, Junot C, Heilier J-F (2011) Applications of liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in clinical chemistry and toxicology: A review. Clin Biochem 44: 119–135 - PubMed
-
- Lindon JC, Holmes E, Nicholson JK (2006) Metabonomics techniques and applications to pharmaceutical research & development. Pharmaceutical research 23: 1075–1088 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
