The role of mitochondria in the development and progression of lung cancer
- PMID: 24688727
- PMCID: PMC3962144
- DOI: 10.5936/csbj.201303019
The role of mitochondria in the development and progression of lung cancer
Abstract
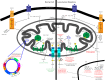
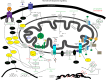
The influence of mitochondria in human health and disease is a rapidly expanding topic in the scientific literature due to their integral roles in cellular death and survival. Mitochondrial biology and alterations in function were first linked to cancer in the 1920s with the discovery of the Warburg effect. The utilization of aerobic glycolysis in ATP synthesis was the first of many observations of metabolic reprogramming in cancer. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer has expanded to include defects in mitochondrial genomics and biogenesis, apoptotic signaling and mitochondrial dynamics. This review will focus on the role of mitochondria and their influence on cancer initiation, progression and treatment in the lung.
Keywords: apoptosis; mitochondrial dynamics; mitochondrial dysfunction; non-small cell lung cancer; tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
The Warburg effect: essential part of metabolic reprogramming and central contributor to cancer progression.Int J Radiat Biol. 2019 Jul;95(7):912-919. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1589653. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019. PMID: 30822194 Review.
-
Revisiting the Warburg effect: historical dogma versus current understanding.J Physiol. 2021 Mar;599(6):1745-1757. doi: 10.1113/JP278810. Epub 2021 Jan 4. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33347611 Review.
-
Mitochondria in cancer.Oncogene. 2006 Aug 7;25(34):4630-2. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209589. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16892077
-
Endocytosis-mediated mitochondrial transplantation: Transferring normal human astrocytic mitochondria into glioma cells rescues aerobic respiration and enhances radiosensitivity.Theranostics. 2019 May 26;9(12):3595-3607. doi: 10.7150/thno.33100. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31281500 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic Alterations in Mitochondrial DNA Are Complementary to Nuclear DNA Mutations in Pheochromocytomas.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 6;14(2):269. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020269. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053433 Free PMC article.
-
Naja Naja Oxiana Venom Fraction Selectively Induces ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Tumor Cells by Directly Targeting Mitochondria.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017 Aug 27;18(8):2201-2208. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.8.2201. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017. PMID: 28843256 Free PMC article.
-
Actinidia chinensis planch polysaccharide protects against hypoxia‑induced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes in vitro.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jul;18(1):193-201. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8953. Epub 2018 May 3. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29750308 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing PD-1 blockade in NSCLC: Reprogramming tumor immune microenvironment with albumin-bound statins targeting lipid rafts and mitochondrial respiration.Bioact Mater. 2025 Mar 7;49:140-153. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.03.003. eCollection 2025 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40124597 Free PMC article.
-
mtTB: A Web-Based R/Shiny App for Pulmonary Tuberculosis Screening.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Mar 18;12:850279. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.850279. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35392603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- (2013) Cancer Fact Sheet N.297 In: Organization WH , editor.
-
- (2012) Cancer Facts and Figures.: American Cancer Society
-
- (2010) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2010 In: Institute NC, editor: U.S. National Institutes of Health
-
- (2011) A Snapshot of Lung Cancer. In: Institute NC , editor: U.S. National Institutes of Health
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
