Plasma IGFBP-2 levels after postoperative combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy predict prognosis in elderly glioblastoma patients
- PMID: 24690948
- PMCID: PMC3972244
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093791
Plasma IGFBP-2 levels after postoperative combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy predict prognosis in elderly glioblastoma patients
Abstract
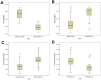
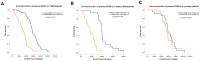
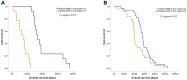
It has been found that preoperative plasma IGFBP-2 levels correlate with prognosis in glioma patients. The prognostic value of plasma IGFBP-2 after postoperative combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy in glioma patients is unknown. Plasma IGFBP-2 levels in 83 glioblastoma patients after postoperative radiotherapy plus chemotherapy were analyzed using an IGFBP-2 ELISA kit. We found that after standard therapy plasma IGFBP-2 levels significantly correlated with the patient's age (R = 0.738, P<0.001) and Karnofsky performance status (KPS, R = -0.633, P<0.05). Cox proportional hazards models were used to calculate hazard ratios (HRs) of death according to plasma IGFBP-2 levels adjusted for patient clinical characteristics. Plasma IGFBP-2 levels significantly correlated with overall survival in glioblastoma patients (multivariate HR = 1.035; 95% CI, 1.024-1.047; P<0.001). The effect of plasma IGFBP-2 levels on survival seemed to differ according to patients' age. Among patients older than 60, high plasma IGFBP-2 levels were associated with a significant increase in overall mortality (HR = 1.097; 95% CI, 1.055-1.140; P<0.001). In contrast, plasma IGFBP-2 levels conferred no significant effect on mortality among patients younger than 60. Elevated plasma IGFBP-2 levels after combined postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy in elderly glioblastoma patients correlate with poor KPS score and predicts poor prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Quaranta M, Divella R, Daniele A, Di TS, Venneri MT, et al. (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor serum levels and prognostic value in malignant gliomas. Tumori 93: 275–280. - PubMed
-
- Malkoun N, Chargari C, Forest F, Fotso MJ, Cartier L, et al. (2012) Prolonged temozolomide for treatment of glioblastoma: preliminary clinical results and prognostic value of p53 overexpression. J Neurooncol 106: 127–133. - PubMed
-
- Natsume A, Kato T, Kinjo S, Enomoto A, Toda H, et al. (2012) Girdin maintains the stemness of glioblastoma stem cells. Oncogene 31: 2715–2724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

