Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism
- PMID: 24692351
- PMCID: PMC4044302
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2013
Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism
Abstract
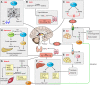
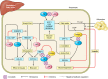
Thyroid hormone (TH) is required for normal development as well as regulating metabolism in the adult. The thyroid hormone receptor (TR) isoforms, α and β, are differentially expressed in tissues and have distinct roles in TH signaling. Local activation of thyroxine (T4), to the active form, triiodothyronine (T3), by 5'-deiodinase type 2 (D2) is a key mechanism of TH regulation of metabolism. D2 is expressed in the hypothalamus, white fat, brown adipose tissue (BAT), and skeletal muscle and is required for adaptive thermogenesis. The thyroid gland is regulated by thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). In addition to TRH/TSH regulation by TH feedback, there is central modulation by nutritional signals, such as leptin, as well as peptides regulating appetite. The nutrient status of the cell provides feedback on TH signaling pathways through epigentic modification of histones. Integration of TH signaling with the adrenergic nervous system occurs peripherally, in liver, white fat, and BAT, but also centrally, in the hypothalamus. TR regulates cholesterol and carbohydrate metabolism through direct actions on gene expression as well as cross-talk with other nuclear receptors, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR), liver X receptor (LXR), and bile acid signaling pathways. TH modulates hepatic insulin sensitivity, especially important for the suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis. The role of TH in regulating metabolic pathways has led to several new therapeutic targets for metabolic disorders. Understanding the mechanisms and interactions of the various TH signaling pathways in metabolism will improve our likelihood of identifying effective and selective targets.
Figures
References
-
- Agellon LB, Drover VA, Cheema SK, Gbaguidi GF, Walsh A. Dietary cholesterol fails to stimulate the human cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 277: 20131–20134, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Aguayo-Mazzucato C, Zavacki AM, Marinelarena A, Hollister-Lock J, El Khattabi I, Marsili A, Weir GC, Sharma A, Larsen PR, Bonner-Weir S. Thyroid hormone promotes postnatal rat pancreatic beta-cell development and glucose-responsive insulin secretion through MAFA. Diabetes 62: 1569–1580, 2013 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Adsani H, Hoffer LJ, Silva JE. Resting energy expenditure is sensitive to small dose changes in patients on chronic thyroid hormone replacement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82: 1118–1125, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Alkemade A, Friesema EC, Kalsbeek A, Swaab DF, Visser TJ, Fliers E. Expression of thyroid hormone transporters in the human hypothalamus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96: E967–971, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

