Transglutaminase regulation of cell function
- PMID: 24692352
- PMCID: PMC4044299
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2013
Transglutaminase regulation of cell function
Abstract
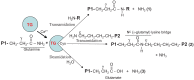
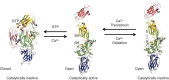
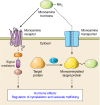
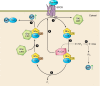
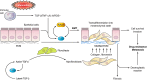
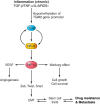
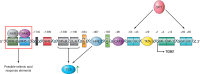
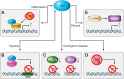
Transglutaminases (TGs) are multifunctional proteins having enzymatic and scaffolding functions that participate in regulation of cell fate in a wide range of cellular systems and are implicated to have roles in development of disease. This review highlights the mechanism of action of these proteins with respect to their structure, impact on cell differentiation and survival, role in cancer development and progression, and function in signal transduction. We also discuss the mechanisms whereby TG level is controlled and how TGs control downstream targets. The studies described herein begin to clarify the physiological roles of TGs in both normal biology and disease states.
Figures




References
-
- AbdAlla S, Lother H, Langer A, el FY, Quitterer U. Factor XIIIA transglutaminase crosslinks AT1 receptor dimers of monocytes at the onset of atherosclerosis. Cell 119: 343–354, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Achyuthan KE, Greenberg CS. Identification of a guanosine triphosphate-binding site on guinea pig liver transglutaminase. Role of GTP and calcium ions in modulating activity. J Biol Chem 262: 1901–1906, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Aeschlimann D, Thomazy V. Protein crosslinking in assembly and remodelling of extracellular matrices: the role of transglutaminases. Connect Tissue Res 41: 1–27, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Ahn JS, Kim MK, Hahn JH, Park JH, Park KH, Cho BR, Park SB, Kim DJ. Tissue transglutaminase-induced down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376: 743–747, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

