Exploring the recent trend in esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality using comparative simulation modeling
- PMID: 24692500
- PMCID: PMC4048738
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-1233
Exploring the recent trend in esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality using comparative simulation modeling
Abstract
Background: The incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) has increased five-fold in the United States since 1975. The aim of our study was to estimate future U.S. EAC incidence and mortality and to shed light on the potential drivers in the disease process that are conduits for the dramatic increase in EAC incidence.
Methods: A consortium of three research groups calibrated independent mathematical models to clinical and epidemiologic data including EAC incidence from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER 9) registry from 1975 to 2010. We then used a comparative modeling approach to project EAC incidence and mortality to year 2030.
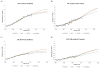
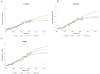
Results: Importantly, all three models identified birth cohort trends affecting cancer progression as a major driver of the observed increases in EAC incidence and mortality. All models predict that incidence and mortality rates will continue to increase until 2030 but with a plateauing trend for recent male cohorts. The predicted ranges of incidence and mortality rates (cases per 100,000 person years) in 2030 are 8.4 to 10.1 and 5.4 to 7.4, respectively, for males, and 1.3 to 1.8 and 0.9 to 1.2 for females. Estimates of cumulative cause-specific EAC deaths between both sexes for years 2011 to 2030 range between 142,300 and 186,298, almost double the number of deaths in the past 20 years.
Conclusions: Through comparative modeling, the projected increases in EAC cases and deaths represent a critical public health concern that warrants attention from cancer control planners to prepare potential interventions.
Impact: Quantifying this burden of disease will aid health policy makers to plan appropriate cancer control measures. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev; 23(6); 997-1006. ©2014 AACR.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures




References
-
- Pohl H, Welch HG. The role of overdiagnosis and reclassification in the marked increase of esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:142–6. - PubMed
-
- Kong CY, Nattinger KJ, Hayeck TJ, Omer ZB, Wang YC, Spechler SJ, et al. The impact of obesity on the rise in esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence: estimates from a disease simulation model. Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention: a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive. Oncology. 2011;20:2450–6. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ye W, Held M, Lagergren J, Engstrand L, Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric atrophy: risk of adenocarcinoma and squamous-cell carcinoma of the esophagus and adenocarcinoma of the gastric cardia. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2004;96:388–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

