Differential regulation of ferritin subunits and iron transport proteins: an effect of targeted hepatic X-irradiation
- PMID: 24693535
- PMCID: PMC3874337
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/353106
Differential regulation of ferritin subunits and iron transport proteins: an effect of targeted hepatic X-irradiation
Abstract
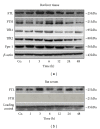
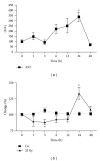
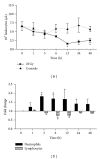
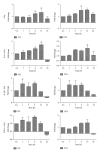
The current study aimed to investigate radiation-induced regulation of iron proteins including ferritin subunits in rats. Rat livers were selectively irradiated in vivo at 25 Gy. This dose can be used to model radiation effects to the liver without inducing overt radiation-induced liver disease. Sham-irradiated rats served as controls. Isolated hepatocytes were irradiated at 8 Gy. Ferritin light polypeptide (FTL) was detectable in the serum of sham-irradiated rats with an increase after irradiation. Liver irradiation increased hepatic protein expression of both ferritin subunits. A rather early increase (3 h) was observed for hepatic TfR1 and Fpn-1 followed by a decrease at 12 h. The increase in TfR2 persisted over the observed time. Parallel to the elevation of AST levels, a significant increase (24 h) in hepatic iron content was measured. Complete blood count analysis showed a significant decrease in leukocyte number with an early increase in neutrophil granulocytes and a decrease in lymphocytes. In vitro, a significant increase in ferritin subunits at mRNA level was detected after irradiation which was further induced with a combination treatment of irradiation and acute phase cytokine. Irradiation can directly alter the expression of ferritin subunits and this response can be strongly influenced by radiation-induced proinflammatory cytokines. FTL can be used as a serum marker for early phase radiation-induced liver damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
x-Irradiation in rat liver: consequent upregulation of hepcidin and downregulation of hemojuvelin and ferroportin-1 gene expression.Radiology. 2007 Jan;242(1):189-97. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2421060083. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Radiology. 2007. PMID: 17090718
-
Reabsorption of iron into acutely damaged rat liver: A role for ferritins.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Nov 7;23(41):7347-7358. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i41.7347. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29151689 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroportin-1 is a 'nuclear'-negative acute-phase protein in rat liver: a comparison with other iron-transport proteins.Lab Invest. 2012 Jun;92(6):842-56. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2012.52. Lab Invest. 2012. PMID: 22469696
-
On Iron Metabolism and Its Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 27;22(9):4591. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094591. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron regulation of ferritin gene expression.J Cell Biochem. 1990 Oct;44(2):107-15. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240440205. J Cell Biochem. 1990. PMID: 2123493 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunosuppressant-Induced Oxidative Stress and Iron: A Paradigm Shift from Systemic to Intrahepatic Abnormalities.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Mar 31;2020:8675275. doi: 10.1155/2020/8675275. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32318243 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-TNF-α antibody infliximab inhibits the expression of fat-transporter-protein FAT/CD36 in a selective hepatic-radiation mouse model.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 2;16(3):4682-97. doi: 10.3390/ijms16034682. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25739082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shim SJ, Seong J, Lee IJ, Han KH, Chon CY, Ahn SH. Radiation-induced hepatic toxicity after radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology Research. 2007;37(11):906–913. - PubMed
-
- Christiansen H, Sheikh N, Saile B, et al. X-irradiation in rat liver: consequent upregulation of hepcidin and downregulation of hemojuvelin and ferroportin-1 gene expression. Radiology. 2007;242(1):189–197. - PubMed
-
- Ramadori G, Christ B. Cytokines and the hepatic acute-phase response. Seminars in Liver Disease. 1999;19(2):141–156. - PubMed
-
- Sheikh N, Dudas J, Ramadori G. Changes of gene expression of iron regulatory proteins during turpentine oil-induced acute-phase response in the rat. Laboratory Investigation. 2007;87(7):713–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

