Hypermethylation in the ZBTB20 gene is associated with major depressive disorder
- PMID: 24694013
- PMCID: PMC4072999
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-4-r56
Hypermethylation in the ZBTB20 gene is associated with major depressive disorder
Abstract
Background: Although genetic variation is believed to contribute to an individual's susceptibility to major depressive disorder, genome-wide association studies have not yet identified associations that could explain the full etiology of the disease. Epigenetics is increasingly believed to play a major role in the development of common clinical phenotypes, including major depressive disorder.
Results: Genome-wide MeDIP-Sequencing was carried out on a total of 50 monozygotic twin pairs from the UK and Australia that are discordant for depression. We show that major depressive disorder is associated with significant hypermethylation within the coding region of ZBTB20, and is replicated in an independent cohort of 356 unrelated case-control individuals. The twins with major depressive disorder also show increased global variation in methylation in comparison with their unaffected co-twins. ZBTB20 plays an essential role in the specification of the Cornu Ammonis-1 field identity in the developing hippocampus, a region previously implicated in the development of major depressive disorder.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that aberrant methylation profiles affecting the hippocampus are associated with major depressive disorder and show the potential of the epigenetic twin model in neuro-psychiatric disease.
Figures
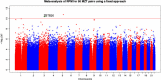


References
-
- Davies MN, Volta M, Pidsley R, Lunnon K, Dixit A, Lovestone S, Coarfa C, Harris RA, Milosavljevic A, Troakes C, Al-Sarraj S, Dobson R, Schalkwyk LC, Mill J. Functional annotation of the human brain methylome identifies tissue-specific epigenetic variation across brain and blood. Genome Biol. 2012;13:R43. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-6-r43. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mill J, Tang T, Kaminsky Z, Khare T, Yazdanpanah S, Bouchard L, Jia P, Assadzadeh A, Flanagan J, Schumacher A, Wang SC, Petronis A. Epigenomic profiling reveals DNA-methylation changes associated with major psychosis. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82:696–711. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.01.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

