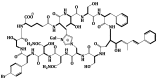
Theonellamide G, a potent antifungal and cytotoxic bicyclic glycopeptide from the Red Sea marine sponge Theonella swinhoei
- PMID: 24694570
- PMCID: PMC4012434
- DOI: 10.3390/md12041911
Theonellamide G, a potent antifungal and cytotoxic bicyclic glycopeptide from the Red Sea marine sponge Theonella swinhoei
Abstract
In our search for bioactive metabolites from marine organisms, we have investigated the polar fraction of the organic extract of the Red Sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. Successive chromatographic separations and final HPLC purification of the potent antifungal fraction afforded a new bicyclic glycopeptide, theonellamide G. The structure of the peptide was determined using extensive 1D and 2D NMR and high-resolution mass spectral determinations. The absolute configuration of theonellamide G was determined by chemical degradation and 2D NMR spectroscopy. Theonellamide G showed potent antifungal activity towards wild and amphotericin B-resistant strains of Candida albicans with IC₅₀ of 4.49 and 2.0 μM, respectively. Additionally, it displayed cytotoxic activity against the human colon adenocarcinoma cell line (HCT-16) with IC₅₀ of 6.0 μM. These findings provide further insight into the chemical diversity and biological activities of this class of compounds.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Theonellamides J and K and 5-cis-Apoa-theopalauamide, Bicyclic Glycopeptides of the Red Sea Sponge Theonella swinhoei.Mar Drugs. 2021 Dec 27;20(1):31. doi: 10.3390/md20010031. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 35049886 Free PMC article.
-
Colony-wise Analysis of a Theonella swinhoei Marine Sponge with a Yellow Interior Permitted the Isolation of Theonellamide I.J Nat Prod. 2018 Nov 26;81(11):2595-2599. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00591. Epub 2018 Oct 22. J Nat Prod. 2018. PMID: 30346758
-
Mirabolides A and B; New Cytotoxic Glycerides from the Red Sea Sponge Theonella mirabilis.Mar Drugs. 2016 Aug 18;14(8):155. doi: 10.3390/md14080155. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27548191 Free PMC article.
-
Solomonamides A and B, new anti-inflammatory peptides from Theonella swinhoei.Org Lett. 2011 Mar 18;13(6):1532-5. doi: 10.1021/ol200221n. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Org Lett. 2011. PMID: 21341715
-
Theonella: A Treasure Trove of Structurally Unique and Biologically Active Sterols.Mar Drugs. 2023 May 8;21(5):291. doi: 10.3390/md21050291. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37233485 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peptides, Peptidomimetics, and Polypeptides from Marine Sources: A Wealth of Natural Sources for Pharmaceutical Applications.Mar Drugs. 2017 Apr 22;15(4):124. doi: 10.3390/md15040124. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28441741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiproliferation Effects of Marine-Sponge-Derived Methanol Extract of Theonella swinhoei in Oral Cancer Cells In Vitro.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 4;11(10):1982. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101982. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290705 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Candidal Marine Natural Products: A Review.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;9(8):800. doi: 10.3390/jof9080800. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37623571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytotoxic Psammaplysin Analogues from the Verongid Red Sea Sponge Aplysinella Species.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 8;9(12):841. doi: 10.3390/biom9120841. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31817954 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal and Antibacterial Activities of Isolated Marine Compounds.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jan 18;15(2):93. doi: 10.3390/toxins15020093. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36828408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schmidt E.W., Harper M.K., Faulkner D.J. Mozamides A and B, cyclic peptides from a Theonellid sponge from Mozambique. J. Nat. Prod. 1997;60:779–782. doi: 10.1021/np970195x. - DOI
-
- Hamada T., Suyawara T., Matsunaga S., Fusetani N. Polytheonamides, unprecedented highly cytotoxic polypeptides from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei 2. Structure elucidation. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994;35:609–612. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)75851-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources