Prevalence of obesity was related to HLA-DQ in 2-4-year-old children at genetic risk for type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 24694666
- PMCID: PMC4185013
- DOI: 10.1038/ijo.2014.55
Prevalence of obesity was related to HLA-DQ in 2-4-year-old children at genetic risk for type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objectives: Body size is postulated to modulate type 1 diabetes as either a trigger of islet autoimmunity or an accelerator to clinical onset after seroconversion. As overweight and obesity continue to rise among children, the aim of this study was to determine whether human leukocyte antigen DQ (HLA-DQ) genotypes may be related to body size among children genetically at risk for type 1 diabetes.
Methods: Repeated measures of weight and height were collected from 5969 children 2-4 years of age enrolled in The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young prospective study. Overweight and obesity was determined by the International Obesity Task Force cutoff values that correspond to body mass index (BMI) of 25 and 30 kg m(-)(2) at age 18.
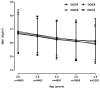
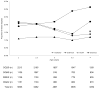
Results: The average BMI was comparable across specific HLA genotypes at every age point. The proportion of overweight was not different by HL A, but percent obesity varied by age with a decreasing trend among DQ2/8 carriers (P for trend=0.0315). A multivariable regression model suggested DQ2/2 was associated with higher obesity risk at age 4 (odds ratio, 2.41; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-4.80) after adjusting for the development of islet autoantibody and/or type 1 diabetes.
Conclusions: The HLA-DQ2/2 genotype may predispose to obesity among 2-4-year-old children with genetic risk for type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tuomilehto J. The Emerging Global Epidemic of Type 1 Diabetes. Current diabetes reports. 2013:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Onkamo P, Vaananen S, Karvonen M, Tuomilehto J. Worldwide increase in incidence of Type I diabetes--the analysis of the data on published incidence trends. Diabetologia. 1999;42(12):1395–1403. - PubMed
-
- Keenan H, el Deirawi K, Walsh M, Grover VV, Alva E, Onyemere K, et al. Are trends in diabetes incidence changing for minority children? Annals of epidemiology. 2000;10(7):459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK95300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700014C/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK100238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK095300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

