High rates of non-adherence to antihypertensive treatment revealed by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HP LC-MS/MS) urine analysis
- PMID: 24694797
- PMCID: PMC4033175
- DOI: 10.1136/heartjnl-2013-305063
High rates of non-adherence to antihypertensive treatment revealed by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HP LC-MS/MS) urine analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Non-adherence to therapy is an important cause of suboptimal blood pressure control but few practical tools exist to accurately and routinely detect it. We used a simple urine-based assay to evaluate the prevalence of antihypertensive treatment non-adherence and its impact on blood pressure in a specialist hypertension centre.
Methods: 208 hypertensive patients (125 new referrals, 66 follow-up patients with inadequate blood pressure control and 17 renal denervation referrals) underwent assessment of antihypertensive drug intake using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HP LC-MS/MS) urine analysis at the time of clinical appointment. A total of 40 most commonly prescribed antihypertensive medications (or their metabolites) were screened for in spot urine samples.
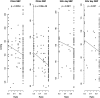
Results: Overall, 25% of patients were totally or partially non-adherent to antihypertensive treatment (total non-adherence 10.1%, partial non-adherence 14.9%). The highest prevalence of partial and total non-adherence was among follow-up patients with inadequate blood pressure control (28.8%) and those referred for consideration of renal denervation (23.5%), respectively. There was a linear relationship between blood pressure and the numerical difference in detected/prescribed antihypertensive medications-every unit increase in this difference was associated with 3.0 (1.1) mm Hg, 3.1 (0.7) mm Hg and 1.9 (0.7) mm Hg increase in adjusted clinic systolic blood pressure, clinic diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and 24 h mean daytime DBP (p=0.0051, p=8.62 × 10(-6), p=0.0057), respectively.
Conclusions: Non-adherence to blood pressure lowering therapy is common, particularly in patients with suboptimal blood pressure control and those referred for renal denervation. HP LC-MS/MS urine analysis could be used to exclude non-adherence and better stratify further investigations and intervention.
Figures

Comment in
-
Resistant hypertension: resistance to treatment or resistance to taking treatment?Heart. 2014 Jun;100(11):821-2. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2014-305540. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Heart. 2014. PMID: 24694796 No abstract available.
-
Response to Kinnell letter.J Anal Toxicol. 2017 Jan;41(1):81. doi: 10.1093/jat/bkw097. Epub 2016 Sep 20. J Anal Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27650311 No abstract available.
References
-
- Steiner JF. Rethinking adherence. Ann Intern Med 2012;157:580–5 - PubMed
-
- Myat A, Redwood SR, Qureshi AC, et al. Resistant hypertension. BMJ 2012;345:e7473. - PubMed
-
- Myat A, Redwood SR, Qureshi AC, et al. Renal sympathetic denervation therapy for resistant hypertension: a contemporary synopsis and future implications. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2013;6:184–97 - PubMed
-
- Corrao G, Parodi A, Nicotra F, et al. Better compliance to antihypertensive medications reduces cardiovascular risk. J Hypertens 2011;29:610–18 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
