Crude ethyl acetate extract of marine microalga, Chaetoceros calcitrans, induces Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
- PMID: 24696543
- PMCID: PMC3969653
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.126650
Crude ethyl acetate extract of marine microalga, Chaetoceros calcitrans, induces Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Marine brown diatom Chaetoceros calcitrans and green microalga Nannochloropsis oculata are beneficial materials for various applications in the food, nutraceutical, pharmaceutical and cosmeceutical industries.
Objective: This study investigated cytotoxicity of different crude solvent extracts from C. calcitrans and N. oculata against various cancer cell lines.
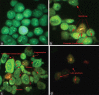
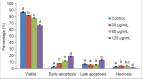
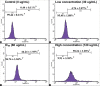
Materials and methods: 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay was carried out to screen the cytotoxic effects of hexane (Hex), dichloromethane (DCM), ethyl acetate, and methanol extract from C. calcitrans and N. oculata toward various cancer cell lines. Flow cytometry cell cycle was used to determine the cell cycle arrest while the mode of cell death was investigated through acridine orange/propidium iodide (AOPI) staining, Annexin V-Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC) and Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated d-UTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) assays. Expression profile of apoptotic and proliferative-related genes was then determined using the multiplex gene expression profiler (GeXP).
Results: Crude ethyl acetate (CEA) extract of C. calcitrans inhibited growth of MDA-MB-231 cells, with IC50 of 60 μg/mL after 72 h of treatment. Further studies were conducted to determine the mode of cell death at various concentrations of this extract: 30, 60 and 120 μg/mL. The mode of cell death was mainly apoptosis as shown through apoptosis determination test. The expression data from GeXP showed that caspase-4 was upregulated while B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2(Bcl-2) was down regulated. Thus, caspase-4 induction endoplasmic reticulum death pathway is believed to be one of the mechanisms underlying the induction of apoptosis while Bcl-2 induced S and G2/M cell cycle phase arrest in MDA-MB-231 cells.
Conclusion: CEA extract of C. calcitrans showed the highest cytotoxicity on MDA-MB-231 via apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Chaetoceros calcitrans; MDA-MB-231; crude ethyl acetate extract; gene expression profiler.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cytotoxic effect of ethanol extract of microalga, Chaetoceros calcitrans, and its mechanisms in inducing apoptosis in human breast cancer cell line.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:783690. doi: 10.1155/2013/783690. Epub 2012 Dec 30. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23509778 Free PMC article.
-
Dillenia suffruticosa dichloromethane root extract induced apoptosis towards MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jul 1;187:195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.04.048. Epub 2016 Apr 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27131434
-
Dicranopteris linearis extract inhibits the proliferation of human breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231) via induction of S-phase arrest and apoptosis.Pharm Biol. 2018 Dec;56(1):422-432. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1495748. Pharm Biol. 2018. PMID: 30301390 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-cancer Effect and Active Phytochemicals of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. against Human Breast Cancer Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Apr 1;24(4):1265-1274. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.4.1265. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37116149 Free PMC article.
-
Increased fucoxanthin in Chaetoceros calcitrans extract exacerbates apoptosis in liver cancer cells via multiple targeted cellular pathways.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2018 Dec 6;21:e00296. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2018.e00296. eCollection 2019 Mar. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2018. PMID: 30581767 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum Activates a Mitophagic Pathway in Human Lung Cancer Cells.Mar Drugs. 2018 Dec 12;16(12):502. doi: 10.3390/md16120502. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30545093 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolite Profiling of the Microalgal Diatom Chaetoceros Calcitrans and Correlation with Antioxidant and Nitric Oxide Inhibitory Activities via ¹H NMR-Based Metabolomics.Mar Drugs. 2018 May 7;16(5):154. doi: 10.3390/md16050154. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29735927 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletonema marinoi Extracts and Associated Carotenoid Fucoxanthin Downregulate Pro-Angiogenic Mediators on Prostate Cancer and Endothelial Cells.Cells. 2023 Mar 30;12(7):1053. doi: 10.3390/cells12071053. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048126 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Microalgae with Anti-Cancer Properties.Mar Drugs. 2018 May 15;16(5):165. doi: 10.3390/md16050165. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29762545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer Compounds Derived from Marine Diatoms.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jul 9;18(7):356. doi: 10.3390/md18070356. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32660006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kornprobst JM. Substances Naturelles D’origine Marine: chimiodiversité, Pharmacodiversité, Biotechnologie. Paris: Lavoisier Publisher; 2005. Spongiaires (Eponges) pp. 601–84.
-
- Tolga G, Yaşar D, Şevket G. Effects of light path lengths and initial culture density on the cultivation of Chaetoceros muelleri (Lemmermann, 1898) Aquaculture. 2003;217:431–6.
-
- Moreau D, Tomasoni C, Jacquot C, Kaas R, Le Guedes R, Cadoret JP, et al. Cultivated microalgae and the carotenoid fucoxanthin from Odontella aurita as potent anti-proliferative agents in bronchopulmonary and epithelial cell lines. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006;22:97–103. - PubMed
-
- Gwo JC, Chiu JY, Chou CC, Cheng HY. Cryopreservation of a marine microalga, Nannochloropsisoculata (Eustigmatophyceae) Cryobiology. 2005;50:338–43. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2010. [Accessed Date 2012 August 11]. GLOBOCAN 2008 v2.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 10. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
